What is an IT Risk Assessment Checklist?
An IT Risk Assessment Checklist serves as a practical framework for organizations to systematically manage security exposures and improve resilience. Its primary purpose is to guide consistent evaluations across technology assets, ensuring that risks are prioritized, controls are validated, and mitigation strategies are well-structured.
A complete risk assessment approach covers critical focus areas such as identifying security risks, safeguarding sensitive data, monitoring insider threats, managing third-party exposures, and meeting compliance requirements. Establishing best practices across these areas helps organizations reduce vulnerabilities, maintain operational stability, and strengthen their long-term security posture.
Why is an IT Risk Assessment Checklist Important?
An IT Risk Assessment Checklist is important because it helps organizations systematically expose hidden risks, strengthen security measures, and maintain resilience across their technology environment.
Below are the 10 primary importance of maintaining a security risk assessment checklist.
- Proactively identify vulnerabilities by focusing assessments on current sensitive assets and critical systems.
- Assess threats systematically to prevent malicious attacks, accidental breaches, and natural disruptions.
- Increase organizational resilience by preparing defenses against cyber attacks, ransomware attacks, and insider threats.
- Develop concrete security controls that secure networks, data, and communication environments.
- Mitigate financial impacts associated with data breaches, compliance penalties, and system failures.
- Ensure compliance with information security frameworks like NIST SP 800-30, HIPAA, and GDPR.
- Drive consistent communication across management, employees, and technology teams regarding security risks.
- Spend organizational resources efficiently by prioritizing threats using a risk matrix approach.
- Learn about emerging threats by conducting regular assessments and maintaining a working inventory.
- Increase trustworthiness and operational reliability through a proficient information technology risk assessment process that stakeholders can verify.
What is the Step-by-Step Process for Performing an IT Risk Assessment?
The step-by-step process for performing an IT risk assessment involves nine specific actions that evaluate exposure points, measure potential impacts, and plan effective security improvements across an organization’s technology environment.
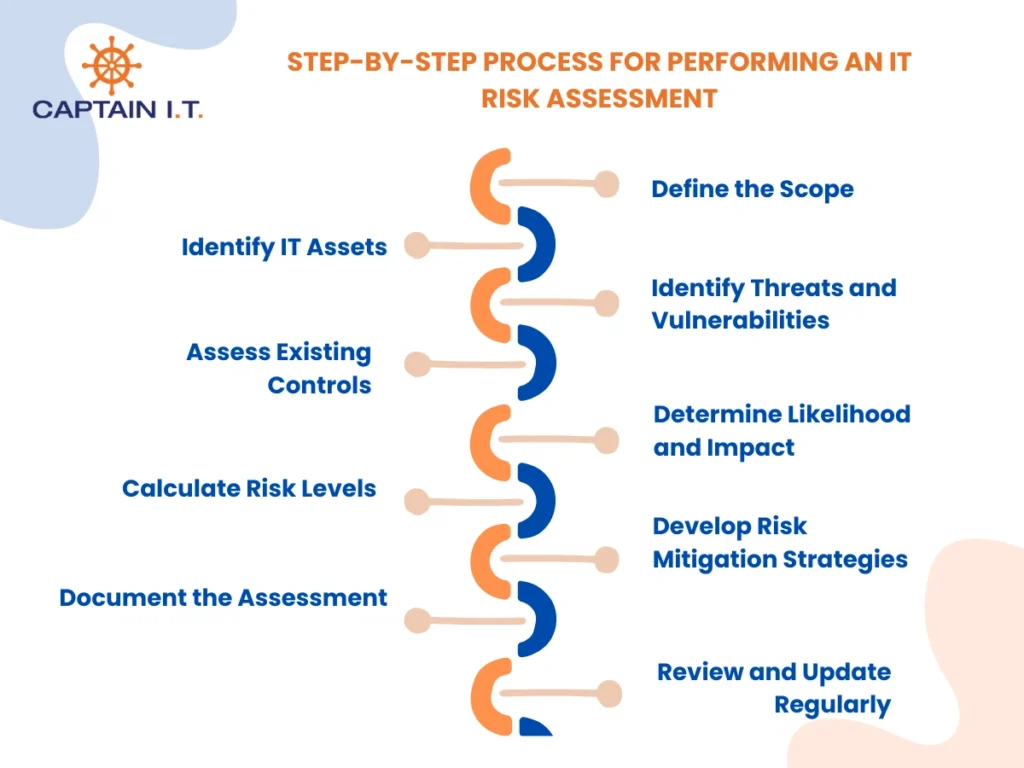
The step-by-step process for performing an IT risk assessment is described below.
- Step 1: Define the Scope
The first step is to define the appropriate boundaries of the risk assessment by identifying all systems, resources, and assets under consideration. Clarifying the scope ensures that the evaluation remains focused and covers all sensitive areas without diluting efforts on non-critical components. - Step 2: Identify IT Assets
After the scope is set, organizations must catalog all IT assets, including hardware, software applications, network devices, and communication systems. Identifying assets consistently is essential because every untracked asset becomes a potential vulnerability in the larger risk management plan. - Step 3: Identify Threats and Vulnerabilities
The next action is to identify the threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise IT assets. Organizations should focus on discovering internal weaknesses, such as misconfigured systems, and external dangers like malicious cyber attacks to develop a complete threat landscape. - Step 4: Assess Existing Controls
Once vulnerabilities are mapped, it becomes critical to assess existing controls that are already in place, such as firewalls, access controls, or backup mechanisms. Evaluating these controls helps in determining gaps and recognizing whether additional defenses are needed to secure critical assets. - Step 5: Determine Likelihood and Impact
Each identified threat-vulnerability pair must be assessed for two factors: likelihood and impact. Likelihood measures how probable it is that the threat will exploit the vulnerability, while impact evaluates the potential financial, operational, or reputational damage. This quick evaluation helps prioritize risks based on their criticality to the organization. - Step 6: Calculate Risk Levels
After determining likelihood and impact, organizations must combine these factors to calculate the overall risk. A high likelihood and high impact indicate a critical risk (High likelihood + High impact = Critical Risk), while a low likelihood and low impact represent an acceptable risk (Low likelihood + Low impact = Acceptable Risk). Using a structured risk matrix helps focus resources on the most urgent and sensitive threats. - Step 7: Develop Risk Mitigation Strategies
Based on the risk calculations, organizations should develop mitigation strategies. These strategies should either eliminate, transfer, reduce, or accept the risk, depending on the organization’s tolerance thresholds and available security resources. - Step 8: Document the Assessment
As risk actions are planned, it is mandatory to document the entire assessment thoroughly. This documentation should include asset inventories, threat-vulnerability mappings, control evaluations, risk calculations, and planned treatments, ensuring a clear and auditable risk management plan. - Step 9: Review and Update Regularly
Organizations must review and update the risk assessment regularly, typically every quarter or year. As technology environments evolve rapidly, continuous updates ensure the assessment stays aligned with emerging threats and new vulnerabilities. Regular reviews help maintain an effective and current risk management posture.
What are the Key Components of an IT Risk Assessment Checklist?
The key components of an IT risk assessment checklist include security controls, data protection, user behavior monitoring, third-party risks, and incident response planning. By evaluating these domains systematically, organizations can strengthen their technology infrastructure, maintain data integrity, comply with regulatory standards, and ensure effective business continuity.
Impact Analysis
Not every threat carries the same weight, and impact analysis helps distinguish which ones could cause business-wide consequences. It doesn’t just focus on financial loss; it examines the broader ripple effects across service delivery, contractual obligations, and stakeholder confidence.
- Categorize assets by operational importance and sensitivity.
- Estimate financial losses per hour of downtime or data breach.
- Identify cross-system dependencies that amplify risk.
- Evaluate non-financial consequences like brand damage or compliance violations.
- Align impact levels with business continuity goals and SLA targets.
Risk Scoring
Whether using a heat map or a formal scoring system, this component converts uncertainty into structured insight. Risk scoring translates a variety of threat indicators into quantifiable values, enabling teams to make priority-based decisions rather than assumptions.
- Define scoring criteria for probability and impact ranges.
- Use a 3×3 or 5×5 risk matrix to visualize threat levels.
- Tag risks as “High,” “Moderate,” or “Low” based on calculated scores.
- Prioritize remediation based on the combined risk score and asset value.
- Apply NIST or ISO-based scoring formulas for standardization.
Security Risks
Assessing security risks begins by examining threats such as cyber attacks, ransomware attempts, and unauthorized access that target critical systems. Recognizing these risks early enables organizations to build resilient defenses and protect sensitive technology environments.
The following checklist items help ensure a complete evaluation of security risks:
- Identify and document all physical and digital assets.
- Assess firewall and antivirus software configurations.
- Evaluate the strength of password policies.
- Confirm the implementation of multi-factor authentication.
- Scan for vulnerabilities in the network and endpoints.
- Review access control lists for least privilege enforcement.
- Inspect for outdated or unpatched software.
- Analyze wireless network security (encryption, segmentation).
- Review remote access configurations (VPN, RDP, etc.).
- Audit logging and monitoring for security events.
Data Risks
Evaluating data risks requires a focus on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of stored and transmitted information. Addressing weaknesses in data management helps prevent breaches, losses, and unauthorized disclosures.
Organizations should review the following checklist components to strengthen their data protection practices:
- Identify where sensitive data is stored, transmitted, or processed.
- Evaluate data encryption policies (at rest and in transit).
- Check backup processes (frequency, coverage, offsite/cloud copies).
- Test data restore procedures.
- Review data retention and disposal policies.
- Verify compliance with data privacy laws (HIPAA, CCPA, GDPR, etc.).
User & Insider Risks
Managing user and insider risks demands close attention to activities performed by employees, vendors, and contractors. Monitoring user behavior helps detect accidental errors and prevent malicious insider threats before they escalate.
The checklist below highlights critical areas for managing user and insider risks:
- Review onboarding and offboarding processes.
- Check user activity monitoring practices.
- Validate user training on cybersecurity awareness.
- Assess privilege creep (unnecessary access rights).
- Evaluate the use of shadow IT (unauthorized apps or systems).
Third-Party & Cloud Risks
Mitigating third-party and cloud risks involves reviewing the security measures of external vendors, partners, and cloud service providers. Strengthening these external relationships ensures that shared resources remain protected from external breaches.
Key checklist activities for assessing third-party and cloud risks include:
- Review vendor risk management and security certifications.
- Assess cloud service configurations (AWS, Azure, M365, etc.).
- Review SLAs and incident response processes with vendors.
- Identify any exposed APIs or integrations.
- Monitor third-party software dependencies.
Infrastructure & System Risks
Identifying infrastructure and system risks starts with assessing the stability and security of networks, servers, hardware devices, and critical technology platforms. Proactive detection of system weaknesses reduces the chances of downtime, service interruptions, and major operational failures.
The following checklist points are essential for evaluating infrastructure and system vulnerabilities:
- Document and evaluate the current network topology.
- Assess patch management and update schedules.
- Review hardware lifecycle and warranties.
- Check for single points of failure in systems.
- Test UPS and power backup systems.
- Evaluate the risk of downtime and disaster recovery planning.
Compliance Assessment & Legal Risks
Addressing compliance and legal risks entails ensuring adherence to regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. Meeting compliance requirements helps organizations avoid legal penalties and safeguard their reputational standing.
Use the following checklist items to assess compliance and legal exposures:
- Identify applicable industry regulations (e.g., HIPAA, PCI-DSS).
- Map existing security controls to legal requirements.
- Validate documentation, access logs, and encryption standards.
- Review audit trails and compliance documentation.
- Flag policy gaps and track remediation progress.
- Assess security policies and incident response plans.
- Ensure acceptable use policies are signed by employees.
- Confirm insurance coverage for cyber incidents.
Incident Response & Recovery
Building incident response and recovery plans centers around preparing for security incidents, minimizing damage, and accelerating recovery times. A structured response framework guarantees business continuity even after disruptive events.
Organizations should focus on these checklist elements to strengthen their incident response and recovery capabilities:
- Review the incident response plan (IRP) documentation.
- Validate communication plans for breach response.
- Test the IRP with tabletop exercises or simulations.
- Assess recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO).
- List mission-critical functions and their RTO/RPO targets.
- Define response roles, escalation paths, and authority levels.
- Document emergency communication procedures for all stakeholders.
- Simulate incidents through tabletop exercises or breach drills.
- Coordinate with disaster recovery and backup procedures.
Ongoing Monitoring & Review
Risks evolve faster than annual assessments can track, which is why continuous observation and iteration are essential. This component transforms security from a periodic project into a live, adaptive process that reflects the current threat landscape.
- Implement SIEM or EDR tools for real-time visibility.
- Track security metrics like MTTD, MTTR, and policy violations.
- Review asset inventory and configurations quarterly.
- Monitor vendor updates, patch cycles, and infrastructure changes.
- Refresh risk assessments after major IT changes or incidents.
What are the Best Practices for Conducting IT Risk Assessment?
Best practices for conducting an IT risk assessment focus on aligning assessments with business objectives, adopting a recognized framework, maintaining an accurate asset inventory, involving key stakeholders, and creating actionable risk treatment plans. Following these structured practices ensures the assessment process remains consistent, targeted, and responsive to changing risk landscapes.
- Align with Business Objectives
Ensure the IT risk assessment supports the organization’s broader strategic goals by prioritizing risks that could impact business operations, financial targets, or regulatory obligations. - Use a Recognized Framework
Base the assessment on recognized standards like NIST SP 800-30 or ISO 27005 to ensure a structured, credible, and repeatable methodology. - Involve Key Stakeholders
Engage executives, IT teams, legal advisors, and business unit leaders to ensure risk identification and prioritization are holistic and accurate. - Maintain an Up-to-Date Asset Inventory
Keep an accurate, current record of all hardware, software, databases, and network assets to ensure no critical elements are overlooked during the risk assessment. - Categorize and Prioritize Risks
Group risks by type and severity, then use a risk matrix to prioritize actions toward the most critical vulnerabilities that threaten key business operations. - Account for Human Factors
Recognize that employees, vendors, and contractors can introduce risks, making it essential to integrate cybersecurity training, activity monitoring, and access control into the risk management plan. - Document Everything
Record all findings, evaluations, decisions, and mitigation plans in structured documentation to ensure auditability, continuity, and regulatory compliance. - Test and Validate Controls
Regularly test existing controls through penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and audit reviews to validate their effectiveness and identify any gaps. - Create Actionable Risk Treatment Plans
Develop specific action plans for mitigating, transferring, accepting, or avoiding risks, each with clear ownership, resources assigned, and defined timelines. - Ensure Compliance with Laws and Regulations
Continuously align risk assessment practices with relevant legal standards like HIPAA, GDPR, or PCI-DSS to avoid fines, penalties, and business interruptions. - Review and Update Periodically
Perform regular reviews, typically quarterly or annually, to refresh the assessment based on new vulnerabilities, technology changes, or business shifts.
Reduce Your IT Risk With an IT Risk Assessment Checklist
An IT risk assessment checklist reduces IT risk by providing a clear framework to uncover hidden weaknesses, validate existing controls, and close security gaps before they escalate into major incidents. Rather than reacting to threats after they occur, businesses use the checklist to proactively strengthen systems and protect critical assets against evolving risks.
To support businesses in managing these challenges, Captain IT offers specialized IT risk assessment services designed to meet the evolving needs of modern organizations. As a trusted managed service provider, Captain IT helps businesses develop tailored risk management strategies, monitor critical assets, and implement proactive defenses to ensure long-term operational resilience and security.












