Information Technology (IT) involves the application of hardware, software, and networking in designing, developing, storing, processing, and transmitting information.
IT involves everything from an operating system to a cloud platform, a database network architecture, and a security system that helps create a strong infrastructure. These interconnected systems are essential for businesses to achieve seamless communications, secure data management, and scalable operations. The extensive applications of IT accompany innovations and ensure efficiency and reliability in critical industries. With this versatility, IT becomes an integral aspect in the health, finance, and education sectors that require workflow management, automation in processing, and invaluable protection of sensitive data. As technology evolves, the demand for professionals such as programming specialists, cloud computing experts, and cybersecurity experts also keeps escalating, opening many rewarding career opportunities.
Careers in IT span from IT Technicians and Network Engineers to Data Scientists, and requires competency in programming, cloud management, and cybersecurity to thrive in the IT industry. Certifications such as AWS Solutions Architect, CISSP, and CompTIA A+ confirm proficiency for succeeding in this transformative field.
How Has Information Technology Evolved Over Time?
Initially centered around simple data processing and on-premise systems, IT boomed in the 1990s when the Internet introduced it to complete global connectivity and real-time collaboration.
The 1990s experienced considerable developments with the first search engine, Archie, in 1990, followed by the launching of Google in 1998, and the first internet-capable mobile device, Nokia 9000 Communicator, in 1996. The 2000s had more transformational innovations like WordPress, YouTube, the first iPhone, and Bitcoin. The 2010s saw the emergence of AI, 5G technology, and quantum computing, and in 2019, Google achieved Quantum Supremacy. The release of ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, and Microsoft-ChatGPT-powered Bing proves that IT plays a consistent part in shaping global communication, automation, and innovation.
Nowadays, technologies such as Cloud Computing enable storage and access to information remotely, while AI automates processes and decisions, and the IoT connects devices with a real-world-based system to allow real-time monitoring and automation. The evolution of IT has completely changed the way businesses and individuals function, communicate, and innovate. It has become indispensable in ensuring communication, data management, and security across all sectors, from smartphones and cloud computing to cybersecurity and automation.
Key Components of Information Technology
Hardware, software, and networking are the three key components of information technology (IT). Together, they constitute the modern IT system for the seamless operations of businesses and individuals in day-to-day life.
Hardware
Hardware is the physical aspect of IT infrastructure, including computers, servers, and networking devices. Computers handle processing tasks, servers manage and store large amounts of data, and networking devices, including routers, facilitate seamless communications and data movements.
Modern hardware segments storage devices such as SSDs, ICT tools such as printers and scanners, and functional components such as CPUs, RAM, and GPUs. Advanced technology products like biometric scans and virtual reality headsets bridge the physical and digital worlds. Hardware assures data processing, safekeeping, and interconnectivity, bringing about operational reliability and seamless integration of business processes. The right kind of hardware ensures that operations flow smoothly while meeting the organizational needs incorporated into IT capabilities.
Software
Software instructs the hardware to execute specific tasks. System software and application software are two primary types of software. System software manages hardware resources through operating systems, while application software streamlines workflows using CRM platforms and productivity tools.
Applications hosted in the cloud, such as Google Workspace, are more dynamic and even physically enhance teamwork and productivity. Software is integral to process automation, increased productivity, actionable insight for smooth delivery, and aligning IT capabilities with business objectives.
Networking
Networking connects machines and systems so they can share information and communicate with each other. It has a wide variety of applications, such as LAN for local connection, WAN, which connects global offices, and, of course, the Internet, which connects customers across the globe. Networking allows the sharing of resources and secures the transfer of data, even real-time collaboration.
Hybrid networking is a network solution capable of effectively mixing on-premises and cloud systems, allowing flexibility and scalability while offering remote work and cloud integration. Networking also makes centralized data administration and secure access possible, which makes it a necessity in contemporary business operations. Networking is central to the digital infrastructure, providing devices and systems with seamless connectivity so businesses can effectively work within a connected world.
Why is Information Technology Crucial in Today’s World?
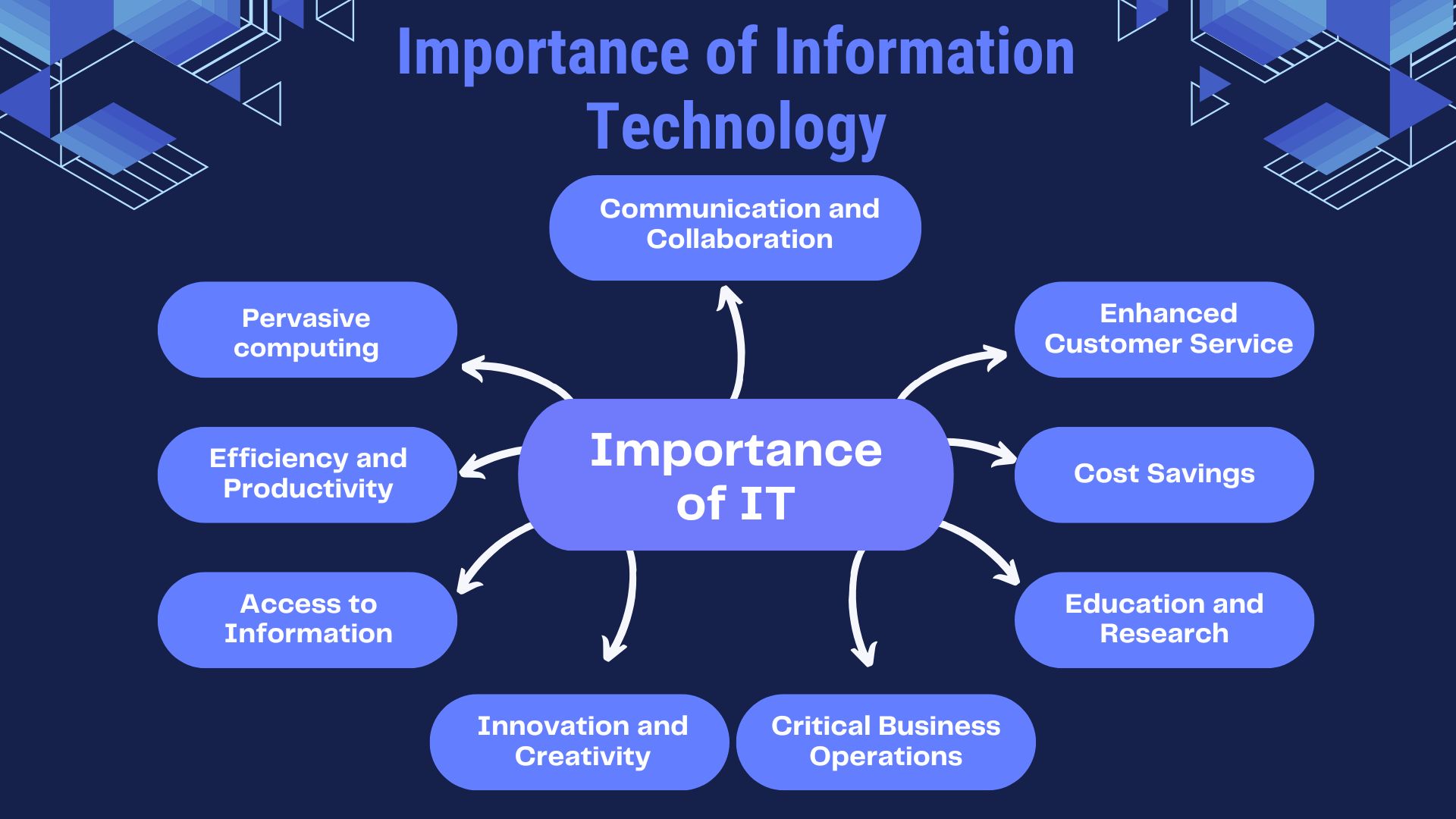
Information technology is vital in today’s world because it facilitates communication, drives innovation, and makes information easily accessible. It is the driving force for enhancing efficiency and productivity that leads to cost savings and delivers exceptional customer service and satisfaction. It helps transform industries and bridge technological gaps in business operations and research.
Communication and Collaboration
Information Technology has brought us to a new level in communication capabilities, with email, video conferencing, and collaborative sites such as Microsoft Teams and Slack providing real-time collaboration for teams dispersed over geographical distances. Cloud-based tools and messaging applications facilitate seamless workflow among employees and support expansion in global workplace culture. IT breaks the geographical barriers that support the interconnectedness of the present economy at a given point.
Pervasive computing
Pervasive computing integrates technology into everyday life through IoT objects, wearables, and smart appliances. Tasks are automated, and personalized experiences improve convenience and enhance productivity. These are hegemonic business applications of pervasive computing that process automation and customer engagement. Individuals can benefit from connected devices, health monitoring, and intelligent home systems that operate on persuasive computing.
Efficiency and Productivity
By automating tasks, information technology optimizes workflows and minimizes errors, which, in turn, enhances productivity. It implements ERP systems, automation platforms, and project management software to prevent operations from wasting time due to delays and reduce operation costs. These productivity tools save employees time and allow them to use them for strategic work. This helps enhance scalability and efficiency in all organizations for growth while enabling businesses to achieve more with fewer resources.
Access to Information
Access to information is made even faster with the use of information technology with cloud storage, search engines, and business intelligence applications such as Tableau. Since reliable data and information can be retrieved right away, problem-solving and informed-decision making can happen at an even faster pace. This is how problems may be made more explicit and more widely discussed, giving power to people and businesses so that they can act effectively and thrive on dynamic challenges.
Innovation and Creativity
With Artificial Intelligence, machine learning, data analytics, and other such technologies, IT drives innovation and creativity in businesses. Organizations use 3D modeling, creative suites, and virtual reality tools to create innovative designs and frameworks. These tools and technologies foster creativity where new trends can be identified, processes can be improved, and unique products can be developed. Providing support for continuous improvement becomes the point of difference for change in the market.
Critical Business Operations
IT utilizes cloud-enabled platforms, cybersecurity solutions, and disaster-recovery tools for seamless business operations. It captures important underlying functions, including financial management, inventory management, and information security, for reliable IT systems that lower risks. Technology advancement and safety improvements in customer relationships are enabled through facilitated technology growth.
Education and Research
The reality of incorporating information technology in education includes virtual classrooms, LMS platforms, and e-learning tools like Moodle. It relies on global resources for research collaboration. It enables learners and researchers to broaden their creative horizons through innovative access to existing knowledge and advanced experimentation tools.
Cost Savings
Automation and optimization-resource technologies make operation and running costs cheaper. Cloud computing, automated, and data analytics tools are available from IT for businesses to scale as needed without overhead costs. For long-term profits, IT creates a space for cost-efficient growth through better financial planning. Streamlined operations will, therefore, eliminate inefficiencies in creating a sustaining environment.
Enhanced Customer Service
IT has technology solutions that improve customer care through CRM systems, chatbot applications, and other link support structures. These allow personalized real-time issue resolution and deliverable feedback. By cultivating a sense of customer satisfaction, loyalty, and trust in the brand, the entire client experience is enhanced, thus sustaining and competing in the market for businesses.
What are the Types of Information Technology?
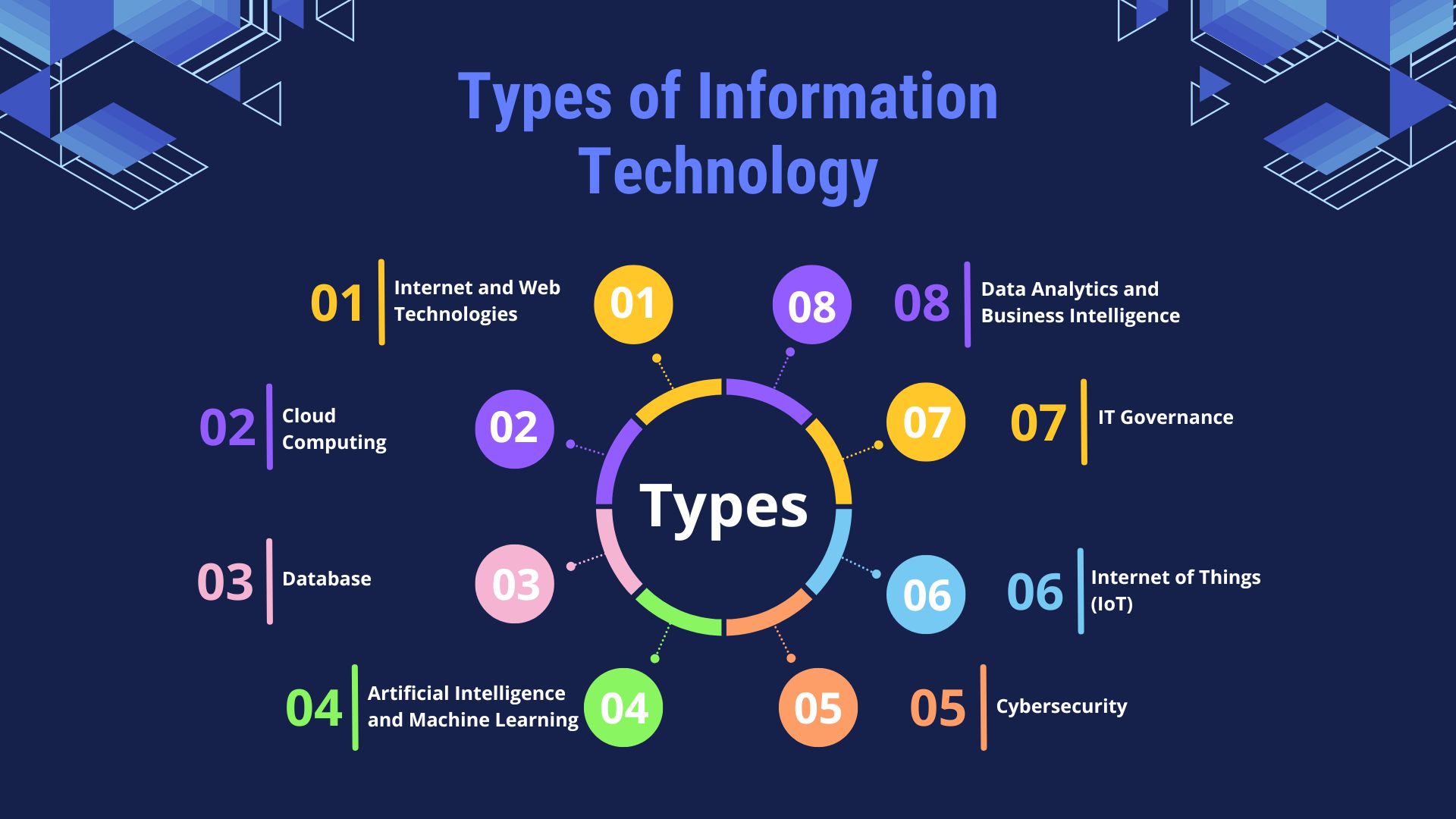
Types of information technology include the Internet and web technologies, cloud computing, databases, artificial intelligence and machine learning, cybersecurity, Internet of Things (IoT), IT governance, and data analytics and business intelligence. The combination of diverse IT types helps create a functioning IT environment for carrying out various daily tasks. They are distinctively important and purposeful for assisting businesses to achieve their goals without wasting effort.
Internet and Web Technologies
Internet and web technologies range from browsers, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to protocols that allow users to view and interact with information on the web. They are the backbone of websites and online platforms, where businesses can build and scale their digital content, user experiences, and collaboration capabilities with dependability and reach.
Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing provides IT resources over the internet, such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, on a pay-per-use basis. Services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer scalable storage, software, and processing solutions with reduced on-site infrastructure costs, enabling any organization to adapt quickly to changing demands.
Database
A database is an IT system that stores organized data for faster retrieval and allows one to access it efficiently. Some examples of popular databases include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. These databases enable high-speed access, relative reporting, and security for data management and are most widely used in businesses to maintain customer data track records, analyze trends, and optimize business operational decisions based on effective analyses to maximize performance.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML enable computers to accomplish activities that previously required human intelligence, such as speech recognition, image analysis, and predictive analytics. These applications that fall from chatbots and autonomous systems to natural language processing include applications in automation, customer support, and trend forecasting for better decision-making.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity safeguards IT systems and data through firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication. These tools prevent unauthorized access and potential cyberattacks to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of business data. This assists organizations in adhering to required security standards and maintaining exceptional customer trust and confidence.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is a network of interconnected devices and sensors that acquire and analyze data in real-time. Smart devices, industrial sensors, and wearables are popular examples of IoT. They help improve the automation and monitoring of healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics industries and deliver efficient insights into business operations.
IT Governance
IT governance defines policies and frameworks such as COBIT and ITIL that align IT resources with the business’s goals. It ensures compliance, optimizes IT investments, and minimizes risks, thus creating a strategic way of managing technology.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence, such as Power BI and Tableau, are analytical tools for studying data trends and patterns. Businesses use data mining, predictive modeling, and predictive frameworks to draw insights, optimize processes, enhance decision-making capabilities, and encourage innovation while improving customer experiences.
Examples of Information Technology
Every sector requires information technology for a diaspora of tasks. Some organizations prioritize one over the other based on their business and technological requirements. E-commerce might need IT for user support, while legal firms might go for tech consulting as it helps satisfy their needs. A wide variety of IT services exists that managed service providers offer as a component of managed IT services. Some examples of information technology are as follows:
-
Security Monitoring
The overall scope of security monitoring comprises the detection, analysis, and reaction to attacks on the network through the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and SIEM software. Continuous uptime in data and networks can be assured through the detection of intrusion activities or attacks from unauthorized entities as well as their prevention and regulatory compliance. It is a major part of a cybersecurity strategy as it is one of the most critical aspects of any organization.
-
Server Upgrade
With server upgrading, the data processing unit speeds up the IT infrastructure and improves reliability while increasing storage capacity. At the same time, it helps facilitate virtualization and cloud migration, bringing more load to the organization without much hassle. Thus, critical performance bottlenecks will also be avoided, and the uptime of the entire business system will be enhanced.
-
Tech Consulting
Tech Consultancy Solutions provides expert advice with regard to developing appropriate IT systems for a certain clientele and expanding the business on the other side. Besides internal projects, consulting services offer the adoption of the cloud, digital transformation, business IT infrastructure planning, and technology alignment with the business in order to work towards strategic executive innovation and utilization of the right investments.
-
New Software
New applications, such as customer relationship management software or ERP building tools, are designed for the automation of workflow or decision-making. However, the scope of customization can range from simple teamwork to finance tracking and extend to fully plug-and-play operational solutions catering to needs for productivity and data management.
-
Business Improvement
Business Improvement harbors business processes that would help satisfy customers’ needs while making good use of available tools like BI software, automation, and data analytical tools. These IT trends would cut costs, increase efficiency, and give you competitive advantages, thus creating room for organizational changes, innovations, and end success.
-
User Support
User support addresses the successful management of IT problems in order to help facilitate the effective operation of hardware and software systems. Specific tools like helpdesk software and remote support platforms enable IT teams to troubleshoot issues quickly. User support increases satisfaction by minimizing downtime and leaving the systems up and running. This contributes to productivity and seamless operations for employees and customers.
-
Backups and Recovery
Backup and Recovery include the tools that secure the information to enable business continuity like disaster recovery as a Service (DRaaS) and cloud solutions. These safeguard the organization against data loss and disruption risks while facilitating a quick recovery from a cyber-attack or system unavailability.
-
Device Procurement
Device acquisitions are obtaining said devices, including servers, computers, and network devices, which include any specific hardware required by a company to operate. An asset management system not only maintains a robust infrastructure but also equips employees with the tools necessary to work securely and efficiently.
-
Business Continuity Planning
Business continuity plans are such crisis management protocols that weigh contingencies like cloud-based computing, duplication of the entire IT infrastructure, and disaster recovery. These thwart disruption otherwise from the business’s operations, guarantee the security of sensitive and critical data and enable the organization’s operational continuity should unforeseen interruptions occur at the workplace.
Real-World Case Studies
The most critical real-world IT case studies are those that demonstrate successful implementations and offer important lessons from failures in the area of IT. These examples inform organizations about the benefits of technology and the essential factors for avoiding pitfalls, ensuring success in the use of IT, and achieving operational efficiencies.
Successful IT Implementations
The results of successful IT implementations show how companies use technology as a growth lever. For example, Old Chang Kee used Microsoft Business Central to increase productivity by 50% and reduce overtime by 30%, and Huber’s Butchery saw revenue growth of 40% and reduced product losses by 10% with SAP Business One. N&N Moving Supplies, in the meantime, reduced payroll processing time by 84% with the help of NetSuite ERP. All can be seen as examples of how custom IT can improve operations and ultimately lead to success.
Lessons Learned from IT Failures
IT failures teach an organization valuable lessons about planning. For instance, Hormel Foods had to contend with operations held up by its legacy systems and poor integration; this case is a clear indicator that a comprehensive strategy is necessary. Green Rabbit proved to be suffering from ineffectiveness by relying on fragmented databases. This shows that these types of systems must provide real-time data analysis. These are lessons about missteps that ultimately cost an organization.
What are the Careers in Information Technology
IT offers you a dynamic spectrum of opportunities from entry-level IT jobs as an IT Technician to advanced jobs like an IT Director. While IT is dynamic in nature, it is open to all kinds of skills and interests so that everyone can find their place in the roles that match their merit. Most IT jobs require basic knowledge, but some require years of experience with appropriate certifications. IT offers boundless potential for growth, be it as a beginner or even if you are looking for a senior position. Some of the major IT careers and what they do, their responsibilities, and required skills are as follows:
-
IT Technician
IT technicians work on keeping all the computers and networks running smoothly, troubleshooting anything wrong with them. Their primary role, however, is mainly installing hardware and configuring software whenever the customer reports a repair. They are experts in providing hardware-fault diagnosis, network maintenance, and efficient and reliable customer service for home and business needs.
-
Support Specialist
Support specialists offer assistance to individuals or organizations so that these users maximize their value from IT. It can be anything from resolving technical queries to solving tech issues to guiding the user on making the most of their technology. Their areas of expertise are problem analysis, troubleshooting, technical solution provision, and communication of improved solution delivery and user satisfaction.
-
Quality Assurance Tester
QA Testers are the actual test monitors. They evaluate software programs in terms of their functionality, reliability, and usability. They prepare test cases, run the test against the developed software, and provide feedback to the development team for improvements. Software testing, bug-tracking, and a keen eye for detail form the bedrock of the product, meeting high-quality standards before it gets to the final release.
-
Web Developer
A web developer creates and optimizes websites and applications with the implication of ease of operation and functionality. Their works are based on various coding languages, such as HTML, JavaScript, and SQL, which are used to produce responsive designs. By honing skills in UI/UX design, database management, and responsive development, they can finally provide a complete digital experience.
-
IT Security Specialist
IT security specialists develop and enforce guidelines for protecting systems and networks from cyber threats. They also conduct security audits. Their proficiency in firewalls, encryption, and threat detection enables them to protect sensitive data, ensure compliance, and respond to breaches.
-
Computer Programmer
A computer programmer writes, tests, and maintains code to make software work. They work with developers and designers to make programs match business needs and user requirements. Key skills include knowledge of languages like Java and Python, debugging, and algorithm development to create software solutions that work and are reliable.
-
Systems Analyst
The systems analyst studies and improves the IT system used by an organization to meet its objectives. They study the processes, design system enhancement, and create collaboration between specific technical teams. The most notable entry skills are business analysis, system design, and project management for proper and optimized IT solutions.
-
Network Engineer
Network Engineers ensure that the designs, implementation, and management of networks provide connectivity and security. They configure routers, troubleshoot issues, and optimize performance. Knowledge of network protocols, VPNs, and firewalls is vital for maintaining smooth communication and secure infrastructures.
-
Software Engineer
Software engineers are persons tasked with developing an efficient application that scales to meet the needs of any business. These engineers primarily write code and test it to ensure the application delivers as promised. They also try to ensure that every functionality works correctly and troubleshoot errors when they occur. C/C++, Agile methodologies, and strategic problem-solving enable them to develop innovative solutions in tune with users’ needs.
-
User Experience Designer
UX Designers create and enhance digital products by doing user research, building prototypes, and testing interfaces. Their understanding of UI design, wireframing, and user research would make any product intuitive, functional, aesthetically pleasing, and encouraging usage.
-
Database Administrator
Database administrators are in charge of maintaining and securing databases and millions of documents. They ensure that the data is properly formatted and can be accessed anytime by required persons. They have different procedures for optimizing performance, doing backups for any eventuality, and troubleshooting the problems the end users encounter. SQL, data security, and performance tuning are core skills that could be indispensable in managing one of the most critical business information sources.
-
Data Scientist
Data scientists generate insights by analyzing a great deal of complex data to determine predictions of future events. They engineer predictive models using machine learning to communicate results using visualizations. Their skills include viewing results in Python, data analysis, and statistical methods that drive data innovation and strategy.
-
Computer Scientist
Computer scientists work to advance technology through research and the development of computation solutions. Algorithms, data structures, and theoretical model constructs are some of the areas they delve into to solve complex problems. Expertise in computational theory, algorithm development, and problem-solving skills is therefore needed for making ground-breaking inventions.
-
IT Director
IT director holds supervision of IT strategy and alignment with business requirements. They control the budgets, supervise the team, and make sure that the infrastructure grows along with it. Strategic Planning, Leadership, and Project Execution skills help take innovation forward and ensure that IT initiatives run successfully in organizations.
Necessary Skills and Certifications in Information Technology
Information Technology is one of the fastest-growing industries, with an estimated growth of 12.5% by 2030. As reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 356,700 job openings emerge for computer and information technology occupations. Professionals in this sector make an average income of $104,420 annually compared to the $48,060 median annual salary in other jobs. One of the reasons for this hype and demand in the market is because of the advancements made in the field, like AI (Artificial intelligence), cloud computing, and cybersecurity, which all require the top technical skills to level up – big data analytics, dev-ops, and mobile app development. Certifications like AWS Certified Solutions Architect and CISSP prove valuable in improving one’s employability and validating one’s knowledge in this dynamic industry. Such certifications empower IT professionals to meet the dynamic real-time needs of the industry and cash in at the moment possible.
What are the Skills needed for a Successful IT Career?
Cybersecurity, cloud computing, edge computing and IoT, IT automation, and software development are major skills needed for a successful IT career. Technical abilities alone cannot aid an IT professional in keeping pace with all the fast-developing emerging technologies within the industry. New technologies now have high demands that require the growing development of skills in big data, AI, and machine learning, to name a few. Understanding and learning new emerging technologies like DevOps would prepare a candidate for the employment battleground and practically enable innovation. These are core IT skills that professionals should learn in the IT domain:
-
Cybersecurity:
Cybersecurity professionals design safety systems and policies that protect organizations and their data against different forms of threats, such as hacking and ransomware. They develop strict ways of ensuring that compliance guarantees the safety of sensitive information in a connected world.
-
Cloud computing:
Cloud computing involves scalable IT as a service over the internet. It cuts down infrastructure spending and makes it more flexible. The professional should have experience with AWS and Azure, among others. This means your business operations can efficiently work remotely and hence be streamlined with improved disaster recovery.
-
Edge Computing and IoT:
While edge computing deals with data as close as possible to its source, IoT connects smart devices for real-time automation and monitoring. Thus, it enables professionals to build a system much more efficiently, reducing latency and enabling innovative changes in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
-
IT Automation:
IT automation uses technology for repetitive tasks, freeing the IT staff to engage in more productive work. Professionals who are competent in automation raise productivity levels to higher ends and improve the long-term efficiency of operations by minimizing human errors and optimizing workflows.
-
Software Development:
Software development entails the design and maintenance of programs that solve business needs. The developers of tools like CRM help many organizations respond to operational challenges in their businesses with increased innovativeness and experience for their employees.
-
Big Data and Analytics:
Big Data and Analytics draw useful insights from vast sets of data that can help drive decisions. Researchers tap into resources such as Tableau and Hadoop to understand trends, enhance process efficiency, and create business advantage through strategic utilization.
-
DevOps:
DevOps is the juncture at which smooth application delivery occurs, where software development and IT operations meet. It would develop professionals who will enable teamwork by automating and hastening top-quality software deployment.
-
AI and Machine Learning:
AI and ML let the system think and decide independently, just like humans. Predictive models and automation created by professionals promise innovation, better customer interaction, and increased productivity for businesses.
-
Mobile App Development:
Mobile application development deals with developing software for handheld gadgets, either smartphones or tablets, with the aim of targeting a mobile-first audience. The professionals design responsive applications for your business to reach out to customers and unlock new avenues of revenue.
Certifications To Earn
Some certifications one should prioritize earning include CompTIA A+, CEH, CRISC, CISM, CCNA, and PMP. Certifications validate technical skills, showcase expertise, and give a competitive edge in the IT industry. With technology ever-changing, certifications ensure that professionals remain abreast with the trends and requirements and are good to go into specialized roles such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, project management, etc. Certifications are also good for honing one’s career but also show commitment to continuing learning, thus making candidates more alluring to employers.
-
AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Professional:
This certification focuses on designing and deploying flexible systems on AWS. It validates specific advanced expertise in cloud architecture, resource optimization, and strategic planning with cloud solutions.
-
CompTIA A+:
Considered a fundamental certification in the field of IT, it is more appropriate for entry-level jobs in IT. Areas of coverage include hardware, software troubleshooting, and networking fundamentals, essentially anything to provide a start in IT.
-
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH):
This also trains students to identify and fix existing security weaknesses. It trains individuals in ethical hacking techniques and tools, building effective organizational defenses against cyber attacks.
-
Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC):
It is all about managing risks from enterprises and implementing controls for IT systems within the enterprise. Therefore, a professional can evaluate existing risks, mitigate them, and manage them to achieve their enterprise objectives.
-
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM):
This certification emphasizes managing and governing enterprise IT security. That is how CISM certification professionals develop security strategies according to an overall business alignment with security policy design and implementation.
-
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP):
This advanced-level course is offered to IT security professionals. It discusses essential topics such as security architecture, risk management, and incident response and is viewed as the gold standard in cyber security expertise.
-
Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA):
CCNA imparts complete and thorough knowledge about the fundamentals of networking, such as routing and switching, and elementary security. It allows professionals to design, troubleshoot, and manage networks within small or medium businesses.
-
Google Certified Professional Cloud Architect:
It guarantees the capabilities of a cloud solution design for Google Cloud. This includes optimizations for the systems, security, and scalability topics, enabling the professional to streamline cloud technologies in alignment with business requirements.
-
Microsoft Role-Based Certifications:
Microsoft also has role-based certifications, such as Azure Administrator and Developer certifications, which focus on end-to-end management and the expertise of an organization in an Azure environment, app building, and its integration into organizations.
-
Project Management Professional (PMP):
This proves the knowledge and proficiency regarding complex projects and dives into best practices for initiation, planning, executing, and closing projects successfully within the constraints of time and budget.
-
VMware Certified Professional:
This includes virtualization and cloud infrastructure training and prepares professionals to manage VMware environments for optimal performance within their scope of operations and scalability.
Which IT Certification Should I Get First?
CompTIA IT Fundamentals, CompTIA A+, CompTIA Network+, CompTIA Security+, and Microsoft Certified Fundamentals are essential IT certifications you should acquire first. It is vital for beginners to make the correct set of certification choices to develop a solid foundation in this field. Entry-level certifications teach concepts such as hardware, networking, and cybersecurity. The entry-level certification provides hands-on experience and enriches the skill set for an IT career. These certifications offer employability at a higher rate in the areas of technical support, networking, and cloud-based functions.
-
CompTIA IT Fundamentals (ITF+):
This is an entry-level certification prepared for people who want to understand the world of IT. Its topics include basic hardware, software, networks, and cybersecurity, forming a foundation for moving on to the more advanced certifications such as CompTIA A+.
-
CompTIA A+:
CompTIA A+ is an entry-level certification globally accepted in the industry for IT professionals. It equips a candidate with troubleshooting hardware, software, and mobile device-related problems, resulting in opportunities for technical support and help desk personnel.
-
CompTIA Network+:
With the CompTIA Network+ certification, you can get started at Building the Foundation for Cisco’s Advanced Certifications by learning the configurations, management, and troubleshooting fundamentals. It forms the bridge to landing jobs such as a Network Administrator and a Systems Engineer.
-
CompTIA Security+:
This qualification gives you the fundamentals of cybersecurity, including risk management and threat mitigation. Globally recognized, security credentials open doors for candidates for Security Analyst and Information Security Specialist jobs.
-
Microsoft Certified Fundamentals:
Microsoft foundational certifications that include subjects like cloud services, data management, and software development prepare candidates for roles such as IT Support or Cloud Administrator in any organization that uses Microsoft technologies.
What IT Jobs Pay the Best?
The executive and senior-level IT jobs with titles like IT Architects, IT Directors, and CIOs pay the best, with annual salaries reaching up to $165,000. Network Engineers and Database Administrators, operating at mid-level, can earn a comfortable yearly income of over $100,000. Entry-level
-
Entry-Level Jobs:
Entry-level roles, such as IT Technician, Junior Developer, and Help Desk Specialist, pay between $40,000 and $85,310 annually. They specialize in system setup, hardware troubleshooting, and resolving user issues. Their responsibility includes managing routine IT operations and addressing tech issues.
-
Mid-Level Jobs:
Mid-level positions offer annual salaries from $80,463 to $124,526. Roles at this level include Network Engineer, System Administrator, and Database Administrator with 4-5 years of experience in the IT industry. They are proficient in managing networks, optimizing IT systems, and ensuring database security. They are also responsible for leading complex tasks, mentoring junior staff, and enhancing system efficiency.
-
Top-Level Jobs:
Top-level IT jobs pay between $123,067 and $165,000 annually. Roles like IT Architect, IT Director, and Chief Information Officer (CIO) are involved in creating advanced IT systems, developing IT strategies, and overseeing large-scale projects like cloud migrations. Executive-level positions directly impact budgeting decisions, vendor management, and technology adoption.
Future Trends in Information Technology
Emerging information technologies, such as IoT and blockchain, reshape the future of industries and rebuild their modes of operation. The Internet of Things (IoT) provides real-time data collection in sectors like health, manufacturing, and smart cities, and it also enables process automation through connected devices. Blockchain increases the level of security and transparency, especially in the financial field, supply chain management, and data sharing. Moreover, IT is modernizing in pursuit of business needs for cloud computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and cybersecurity while innovating, making operations efficient, and informing decision-making based on data. These improvements position IT at the center of enabling digital transformation and opening up great global perspectives for businesses.
Conclusion
Information technology leads each new innovation, helping industries with automation, connectivity, and data management. Be it communication, cybersecurity, or cloud solutions, it changes how every business and individual interacts in a digital-first world. IT presents unparalleled growth opportunities, with AI, IoT, and Blockchain taking center stage in career building. Whether complex problem-solving fascinates you or the art of enabling business transformation, IT is one such domain that just provides a platform to deliver value for you. If you are inspired to explore this dynamic field, acquire the necessary competencies and certifications to help you thrive in this booming industry and begin your IT journey today.