Data security is the practice of protecting digital information throughout its lifecycle from unauthorized access, misuse, alteration, or loss by ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It focuses on safeguarding personal data, financial records, intellectual property, and confidential business information across cloud platforms, internal systems, remote environments, and applications. As data volumes grow rapidly and become more distributed, data security helps prevent unauthorized access, misuse, and data loss for organizations of all sizes, including SMBs.
In practice, businesses rely on a combination of controls and processes to effectively secure data. These include encryption, access management, data loss prevention, continuous monitoring, backups, and incident response procedures. Working together, these data security measures allow organizations to classify data, apply layered protections, detect threats early, and meet legal and regulatory requirements as risks evolve.
Strong data security delivers both protection and business value, reducing the risk of data breaches, ransomware, insider threats, and permanent data loss while supporting compliance and brand trust. By following proven best practices and adopting emerging approaches such as AI-driven detection, Zero Trust models, and quantum-safe encryption, businesses can maintain secure, resilient operations in a data-driven world.
Why is Data Security Important for Modern Organizations?
Data security plays a critical role in protecting sensitive information, including personal data, financial records, and confidential business information, across cloud platforms and internal systems. As organizations generate and store more data, sensitive assets such as intellectual property and personally identifiable information (PII) are increasingly spread across cloud services, applications, laptops, and edge devices, expanding the attack surface and increasing exposure to cyber threats.
For small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs), weak data security can be especially damaging because limited resources often increase exposure to data breaches, unauthorized access, and data loss. As reported by IBM, in 2025, the global average cost of a data breach reached USD 4.4 million, an impact many SMBs struggle to absorb. Strong data security helps prevent fraud, reduce recovery costs, and support business continuity by enabling faster response and recovery during security incidents.
Data security is also essential for industries that handle highly sensitive data, such as healthcare, where protecting patient records is critical to safe and compliant operations. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and SOX mandate encryption, access controls, and secure data handling. By meeting these requirements, organizations reduce regulatory and financial exposure while maintaining customer trust and operational stability.
What Are the Types of Data Security?
Common types of data security include encryption, data masking, data erasure, data loss prevention, data backups, and firewalls to protect digital information. All of these data security types are built around the core principles of Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA), ensuring that data remains protected and accurate for both SMBs and larger enterprises.
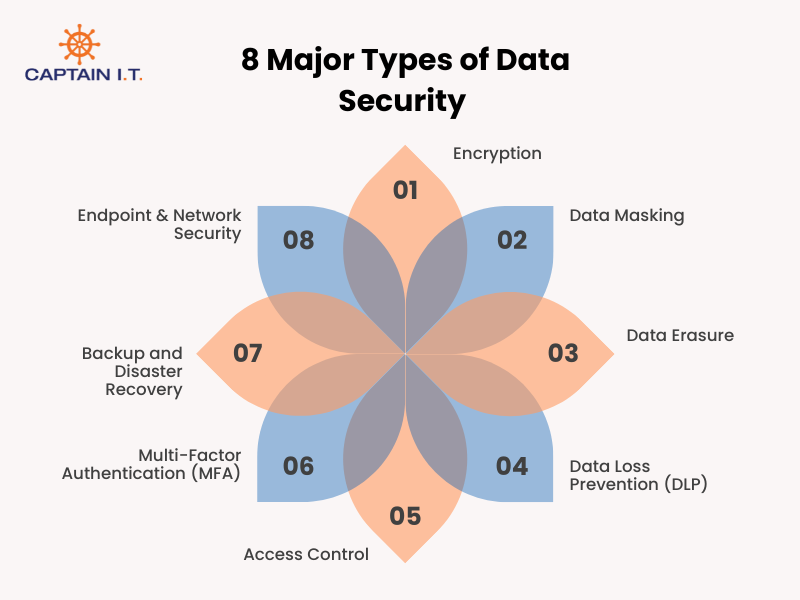
8 major types of data security:
- Encryption: Relies on key management and decryption controls to convert readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) so unauthorized users cannot access it.
- Data Masking: Covers sensitive data elements, such as PII or credit card numbers, by replacing them with fictitious yet structurally similar data
- Data Erasure: Permanently removes data from storage devices using secure deletion methods, ensuring sensitive information cannot be recovered when systems are retired, repurposed, or decommissioned.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Monitors and controls data movement to prevent unauthorized sharing, transfer, or leakage of sensitive information outside the organization.
- Access Control: Restricts who can view, modify, or manage data based on defined user roles and permissions, ensuring access is limited to authorized individuals.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requires users to verify their identity using two or more factors, such as a password and a one-time code, adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Creates secure copies of data and ensures it can be restored after cyberattacks, system failures, or accidental deletion, supporting business continuity.
- Endpoint & Network Security: Protects devices and network infrastructure using firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection systems, and network monitoring to prevent unauthorized access, malware infections, and network-based attacks.
How Do Data Security Systems Work?
Data security systems follow a continuous process that identifies and classifies data, applies layered defenses, monitors for threats, responds to incidents, enforces policies, and updates protections as risks evolve. This approach ensures sensitive data remains protected throughout its lifecycle while supporting compliance, availability, and operational stability for businesses of all sizes, including SMBs.
Key Stages of How Data Security Systems Work:
- Discover and Classify Data: Identifies and categorizes data by sensitivity, value, and risk, ensuring the appropriate security controls are applied to each data type.
- Apply Multiple Layers of Defense: Implements layered security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and firewalls, so that if one control fails, others continue to protect the data.
- Monitor for Threats in Real-Time: Continuously monitors systems for suspicious activity using tools such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) to identify potential threats early.
- Respond to Security Incidents: Activates an incident response process to isolate threats, investigate the impact, and recover compromised or lost data as quickly as possible.
- Enforce Policies and Maintain Compliance: Applies internal data security policies and aligns controls with regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA to protect sensitive information and reduce legal risk.
- Regularly Update Security Measures: Updates tools, configurations, and protocols on an ongoing basis to address new vulnerabilities and emerging threats, ensuring data protection remains effective over time.
What Are the Benefits of Data Security for Businesses?
Strong data security delivers clear benefits to both SMBs and larger companies by protecting sensitive information, strengthening customer confidence, complying with regulations, and preventing financial loss. By implementing effective data security measures, organizations reduce exposure to cyber threats, meet regulatory obligations, and create a more stable and trustworthy operating environment.
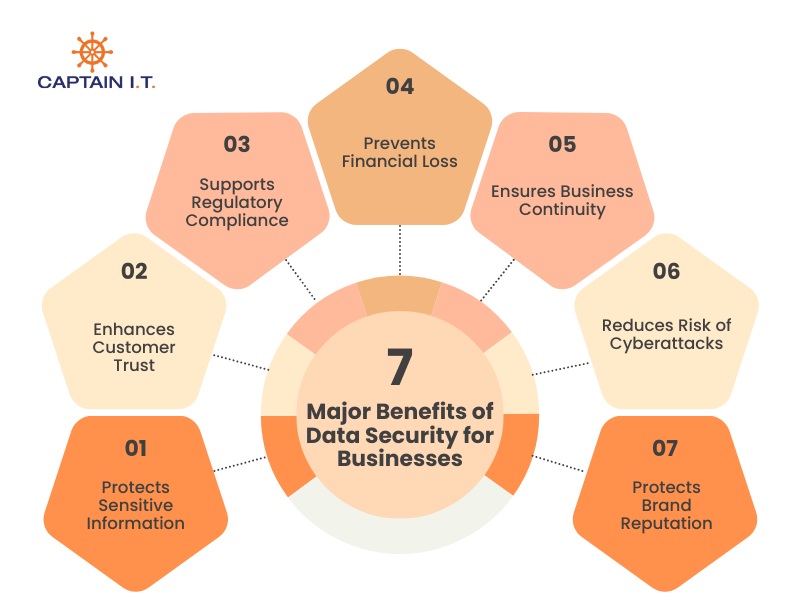
7 major benefits of data security for businesses:
- Protects Sensitive Information: Prevents unauthorized access to personal data, financial records, and confidential business information through controls such as encryption and access management.
- Enhances Customer Trust: Builds customer confidence by demonstrating that personal and business data is handled securely and responsibly.
- Supports Regulatory Compliance: Helps organizations meet legal and regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA, reducing the risk of fines and compliance violations.
- Prevents Financial Loss: Reduces losses caused by data breaches, fraud, and cyberattacks, including recovery costs, legal fees, and lost revenue.
- Ensures Business Continuity: Enables organizations to continue operations during security incidents by supporting rapid data recovery and system availability.
- Reduces Risk of Cyberattacks: Limits exposure to threats such as ransomware and malware by implementing protective controls, including firewalls, monitoring, and encryption.
- Protects Brand Reputation: Demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding data, helping preserve brand credibility, customer loyalty, and long-term business relationships.
What Risks Do Organizations Face Without Data Security?
Without effective data security, small businesses and enterprises (SMEs) expose their data, systems, and operations to serious risks, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, data loss, and reputational damage. Limited security resources and growing attack surfaces further increase vulnerability, making even a single incident capable of disrupting operations, triggering financial losses, and eroding customer trust.
Key risks organizations face without data security:
- Data Breaches: Occur when an unauthorized individual gains access to sensitive data, resulting in the exposure or theft of personal, financial, or confidential business information.
- Ransomware Attacks: Involve malicious software that encrypts organizational data and demands payment to restore access, often causing operational downtime and financial loss.
- Insider Threats: Originate from employees, contractors, or partners who intentionally or unintentionally compromise data security through misuse, negligence, or unauthorized access.
- Permanent Data Loss: Data that is irretrievably lost due to cyberattacks, system failures, or accidental deletion significantly impacts business operations and recovery efforts.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Involves unauthorized access to valuable business assets such as patents, trade secrets, or proprietary data, leading to competitive and financial losses.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Results from failing to meet data protection requirements under regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, exposing organizations to legal action and reputational harm.
- Financial Penalties: Includes fines, lawsuits, and enforcement actions imposed under data protection laws such as the California Consumer Privacy Act, increasing financial strain on the business.
- Reputational Damage: Occurs when security failures erode customer trust, weaken brand credibility, and reduce the organization’s ability to retain and attract customers.
Data Security in Different Environments
Depending on the data security environment, different data security measures are used, including cloud computing, healthcare, finance, express, remote, and e-commerce. Each environment introduces distinct risks, regulatory obligations, and operational challenges, requiring organizations to apply tailored data security controls rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
Key Data Security in Different Environments:
- Cloud Computing Security
Operating under a shared responsibility model, cloud platforms require organizations to secure their data while providers protect the underlying infrastructure. Risks such as misconfigured storage and account hijacking make encryption and strong identity and access controls essential. - Healthcare Data Security
Protecting patient information and Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is a primary requirement in healthcare environments. Therefore, HIPAA compliance depends on encryption, audit trails, and strict access controls to maintain confidentiality and data integrity. - Financial Services Security
Financial institutions are a primary target for cybercriminals due to the immediate liquidity of financial data. Compliance with PCI DSS and SOX is mandatory, necessitating high-level encryption, real-time fraud detection, and hardware security modules (HSMs) to protect transactions and banking records. - Enterprise Data Security
Large-scale organizations face the challenge of data silos across various departments. Enterprise data security focuses on unified network security, overarching governance policies, and centralized access controls to ensure that corporate intelligence and employee data are protected consistently across the entire global infrastructure. - Remote Work Security
Remote environments require secure endpoints, VPNs, and strict access controls to protect sensitive data accessed from home networks and remote locations. Since employees often use personal devices and unsecured Wi-Fi, organizations must enforce endpoint protection, device authentication, and multi-factor authentication to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. - E-commerce Data Security
Online retailers must secure a high volume of credit card transactions and personal shipping details. Beyond PCI DSS compliance, e-commerce platforms implement SSL/TLS certificates for secure browsing and deploy sophisticated anti-fraud tools to detect and block suspicious purchasing patterns in real time.
What Are the Data Security Standards and Compliance Requirements?
Data security standards are structured guidelines, such as ISO/IEC 27001 and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, that define best practices for managing and protecting sensitive data. Compliance requirements are legally binding regulations, including the GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS (payment card data), that mandate how data must be secured to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Adhering to these standards and laws helps organizations protect information assets, reduce data breach risk, avoid financial penalties, and demonstrate accountability to customers, regulators, and partners.
Key Data Security Standards and Compliance:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): An EU regulation that governs how organizations collect, process, and protect personal data of EU residents, requiring strong data security controls, transparency, and breach reporting.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Mandates safeguards for electronic health information, with a focus on maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and controlled access of patient data.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): Set of security requirements designed to protect credit card data by enforcing secure handling, processing, transmission, and storage of payment information.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Part of the US law that enforces strict controls over financial reporting and data integrity, requiring organizations to secure financial records and maintain accurate, reliable data.
- Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA): A US federal law that requires government agencies and contractors to secure information systems and protect federal data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- ISO/IEC 27001: Establishes a risk-based framework for creating, implementing, and maintaining an information security management system (ISMS).
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A framework developed by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology that provides guidelines for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity risks.
- International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR): Regulates access to defence-related technologies and data, requiring organizations to protect sensitive military information and restrict unauthorized export.
What Are the Best Practices That Organizations Should Follow for Data Security?
The best practices that organizations should follow for data security include regular data audits, clear security policies, strong access controls, and encryption of sensitive data. Together, these practices help protect sensitive information, reduce security risks, support compliance requirements, and ensure data remains secure throughout its lifecycle.
9 best practices for data security:
- Conduct Regular Data Audits: Review where data is stored, how it is accessed, and who can use it to identify vulnerabilities, validate controls, and support compliance with security standards.
- Develop a Data Security Policy: Establish clear rules for handling, storing, sharing, and protecting data so employees and partners follow consistent security expectations.
- Implement Access Controls: Enforce role-based permissions and strong authentication to ensure only authorized users can access or modify sensitive data.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Protect data by converting it into an unreadable format, ensuring intercepted or stolen data cannot be accessed without decryption keys.
- Deploy Monitoring and Detection Tools: Use tools such as intrusion detection systems to continuously monitor activity and identify potential threats in real time.
- Create an Incident Response Plan: Define clear steps for detecting, containing, and recovering from security incidents to minimize damage and restore operations quickly.
- Train Employees on Security Practices: Provide ongoing training to ensure employees understand their data security responsibilities, recognize threats, and follow established protocols.
- Maintain Regulatory Compliance: Stay aligned with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA to avoid penalties and legal exposure.
- Collaborate with Trusted Providers: Work with reliable cybersecurity service providers that meet strict security standards and help strengthen the overall data security infrastructure.
What Are the Future Trends in Data Security?
Future data security trends focus on AI and machine learning for threat detection, Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), quantum-safe encryption, and automated security responses. Together, these approaches help organizations proactively defend against advanced threats, reduce reliance on manual processes, and protect sensitive data in increasingly complex and distributed environments.
Key Future Trends in Data Security:
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: By analyzing large volumes of security data, AI and ML models can identify abnormal patterns, predict potential vulnerabilities, and accelerate threat detection and response.
- Zero Trust Security Models: Instead of relying on perimeter-based defenses, ZTA continuously verifies users, devices, and applications, assuming threats can exist both inside and outside the organization.
- Quantum-Safe Encryption: New cryptographic techniques such as lattice-based cryptography are being developed to protect sensitive data from future risks posed by quantum computing, which could compromise traditional encryption methods.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Techniques such as data anonymization and differential privacy allow organizations to analyze data while minimizing exposure of personal and sensitive information.
- Automated Security Response: Real-time automation enables faster identification, containment, and remediation of security incidents, reducing response times and limiting the impact of cyber threats.