IT outsourcing is the practice of using an external Managed Service Provider (MSP) to handle IT operations like software development, network management, cybersecurity, and help desk support. SMBs rely on MSPs to access advanced technical expertise, reduce internal workload, and eliminate the need for in-house teams. The growing demand for IT outsourcing is reflected in market growth, with the industry valued at $588.38 billion in 2025 and projected to reach $806.55 billion by 2030, according to Statista.
Outsourcing arrangements vary by structure and location. Businesses may choose offshore, onshore, or nearshore providers based on cost, communication needs, and regulatory alignment. They can also adopt full-stack outsourcing, selective outsourcing, or ongoing managed IT service agreements depending on how much operational responsibility they want the vendor to handle.
The primary benefits of outsourcing include cost control, specialized expertise, resource scalability, and an improved focus on core business objectives. Pricing commonly follows time-and-materials, fixed-cost, or performance-based models. While outsourcing comes with significant advantages, SMBs must plan for data security, communication gaps, and vendor reliability to achieve consistent long-term value.
What Are the Different Types of IT Outsourcing?
IT outsourcing can be classified into offshore, onshore, and nearshore outsourcing, with each defined by the provider’s geographical location and relationship with the business. These options offer different operational, financial, and communication advantages, and the right choice depends on priorities such as cost control, data security, ease of collaboration, and time zone alignment.
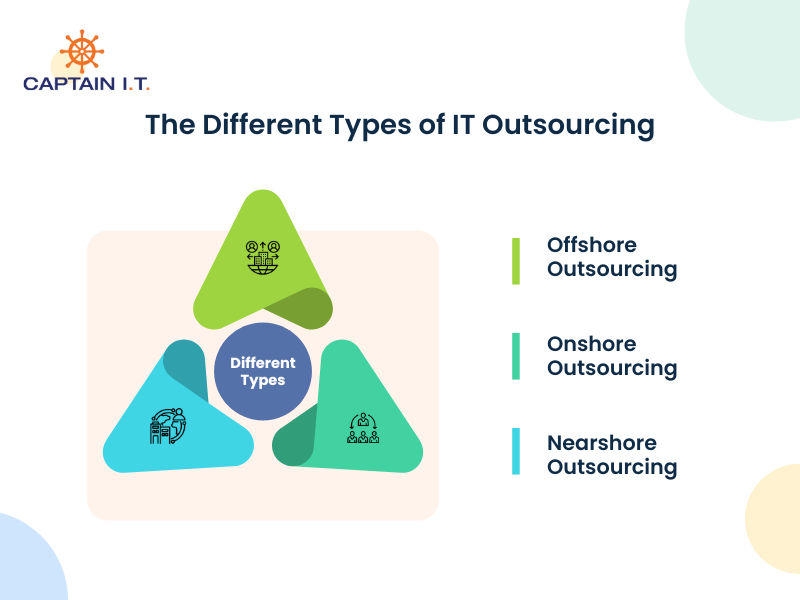
Offshore Outsourcing
Companies can delegate partial or full IT functions to providers in distant countries with lower labor and infrastructure costs, often operating through offshore development centers or BPO hubs. This model supports software development, data processing, quality assurance, and 24/7 support through skilled teams in regions such as India, the Philippines, and Ukraine. Such service providers manage projects through structured workflows and remote coordination. However, it comes with challenges such as time zone gaps, slower feedback cycles, and cultural differences. These issues can be reduced by setting overlapping work hours, using centralized project management tools, and involving onshore coordinators to improve workflow alignment.
Onshore Outsourcing
Domestic or onshore outsourcing relies on service providers within the same country to handle cybersecurity, network monitoring, software maintenance, and help desk support. Businesses choose this model when handling confidential data or projects requiring fast turnaround and in-person coordination, making it suitable for industries like healthcare and finance that must meet HIPAA or SOC 2 standards. Although it costs more than offshore options, onshore outsourcing reduces communication risks and compliance issues because domestic providers operate under the same regulatory environment. Regular performance reviews, clear escalation paths, and structured planning sessions help businesses maintain quality and ensure timely delivery of domestic outsourced projects.
Nearshore Outsourcing
Working with providers in nearby countries allows businesses to collaborate in similar time zones, making coordination easier for development, cloud support, and help desk operations. Through nearshore outsourcing, U.S. companies often partner with teams in Mexico or Costa Rica, while European firms outsource to Poland or Portugal where labor and resource costs are lower. This method enables smoother communication due to overlapping work hours and smaller cultural differences. Despite these benefits, challenges such as differing legal requirements or occasional language gaps still persist. These can be managed by verifying compliance standards, involving bilingual project managers, and maintaining unified documentation and quality controls across teams.
Common IT Services to Outsource
Organizations commonly outsource software development, infrastructure and cloud management, cybersecurity services, and help desk operations. Delegating these functions to external providers help businesses access specialized skills, stronger system reliability, and additional technical capacity. This helps companies streamline their operations and maintain consistent service performance without expanding internal IT teams.
Software Development
Outsourced software development includes activities such as requirements analysis, UI/UX design, coding, testing, and deployment managed by external development teams. These teams use React, .NET, Java, and Python frameworks and rely on DevOps pipelines with tools such as Git, Jira, and Jenkins to build apps, enterprise systems, APIs, and integrations. Many organizations outsource to India or Eastern Europe to access large talent pools with lower development costs. Although this accelerates the development process, businesses must manage time zone differences, code quality, and IP protection through clear documentation, milestone reviews, regular monitoring, and secure development practices.
Infrastructure and Cloud Management
External providers manage IT infrastructure by configuring, monitoring, and securing systems across platforms such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. Their work includes handling virtual machines, storage, backups, firewalls, and network components while ensuring uptime, regular patching, and disaster recovery readiness. MSPs also support capacity planning and cloud cost management through automated monitoring tools. Although outsourcing reduces capital investment in servers and data centers, businesses must maintain strong SLAs, clear access controls, and routine audits to prevent misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and rising cloud costs.
Cybersecurity Services
Partnering with specialized cybersecurity providers strengthens an organization’s defense against digital threats through continuous monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and incident response. Outsourced Security Operations Centers (SOCs) use SIEM platforms, intrusion detection tools, and threat intelligence feeds to identify risks across networks, endpoints, and cloud environments. These vendors also perform penetration testing, phishing simulations, and compliance audits for GDPR, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001 frameworks. Although outsourcing cybersecurity enhances protection through certified analysts and advanced security tools, businesses must verify vendor credentials, define breach response expectations, and maintain strict data governance policies to reduce the risk of security incidents.
IT Support and Help Desk
Outsourced IT support teams manage an organization’s technology-related inquiries and resolve technical issues through a tiered support structure. Level 1 handles basic requests like password resets, software updates, and common troubleshooting, level 2 addresses more advanced problems, and level 3 involves specialized engineers for complex system issues. Providers use ticketing systems, remote access tools, and diagnostic software to deliver quick support for employees and customers. Many organizations rely on offshore help desks in regions like the Philippines or South Africa for 24/7 multilingual coverage. To maintain consistent quality, businesses should define clear escalation steps, maintain an updated knowledge base, and monitor response and resolution times.
What Are the Different IT Outsourcing Models?
The main IT outsourcing models are full-stack outsourcing, selective outsourcing, and managed IT services, each granting different levels of responsibility and control to external providers. Full-stack outsourcing transfers all IT functions to one vendor, selective outsourcing assigns only specific tasks, and managed IT services deliver continuous monitoring and support through a long-term agreement. These models help organizations match their outsourcing approach with technical needs and resource capacity.
Full-Stack Outsourcing
In a full-stack outsourcing arrangement, a business transfers all IT operations to a single vendor that manages infrastructure setup, app development, system maintenance, security monitoring, and ongoing support. Coordinating these functions under one provider creates a central point of accountability, improves system integration, and reduces the complexity of managing multiple service partners. Small and mid-sized businesses often adopt this model when they want a complete, end-to-end technology strategy without maintaining internal IT teams. However, relying on one vendor creates dependency, so it is important to conduct frequent performance reviews, negotiate clear service terms, and maintain detailed SLAs to ensure long-term stability.
Selective Outsourcing
Selective outsourcing allows organizations to outsource only certain IT functions while keeping other responsibilities in-house. This approach helps fill skill gaps in areas like cloud migration, cybersecurity operations, software development, or data recovery. For example, a business may outsource its disaster recovery and backup management to a provider with advanced infrastructure while retaining internal oversight of application support. Its targeted nature improves cost control and provides access to niche expertise, but it also requires strong coordination across vendors to prevent miscommunication or duplicated efforts. Establishing clearly defined roles, shared documentation, and aligned workflows ensures a cohesive collaboration.
Managed IT Services
Organizations that require continuous IT support rely on managed IT services for consistent monitoring, maintenance, and system optimization. In this model, a Managed Service Provider (MSP) oversees core functions such as network administration, endpoint security, cloud management, and help desk operations on an ongoing basis. This proactive structure helps reduce downtime, make costs predictable, and support business stability without the need for internal technical teams. Many companies choose this approach due to its reliability and operational consistency. But in order to maintain full accountability, businesses must establish detailed SLAs that define performance metrics, response expectations, and escalation procedures.
What Are the Benefits of IT Outsourcing?
Partnering with external IT providers helps reduce costs, access specialized expertise, scale resources, and improve operational efficiency. This strategy allows businesses to align technology functions with core objectives, ensuring flexibility, reliability, and scalability in day-to-day operations.
Reduce Operational Costs
Outsourcing IT functions eliminates the need to hire and train full-time staff or invest heavily in scaling or maintaining infrastructure. Many SMBs benefit from this because MSPs reduce the need for in-house teams, hardware replacements, and licensing overhead. A relevant example is Wells Fargo, which outsources large portions of its customer support operations to teams in India and the Philippines, significantly lowering labor costs while maintaining high-volume service delivery. Similar cost advantages apply when companies outsource network management or help desk operations. These savings allow businesses to allocate more capital toward product innovation and market growth.
Access Specialized Expertise
External IT providers supply specialized skills that are difficult or expensive to maintain internally, including cloud engineering, cybersecurity, software development, and analytics. High-growth tech companies and regulated industries benefit most because outsourcing gives them access to certified experts and advanced tools. For instance, Google outsources large parts of its IT infrastructure management and software development to firms in India, allowing it to leverage broader talent pools and accelerate delivery without expanding internal teams. This access speeds up implementation of new solutions, improves system accuracy, and strengthens and organization’s overall technical capacity.
Scale Resources Flexibly
Outsourcing allows organizations to expand or reduce IT resources quickly without hiring or downsizing internal staff. MSPs offer large, distributed teams that can add capacity on demand, which benefits e-commerce, SaaS, and service companies that experience fluctuating workloads. Google’s contractor-based workforce demonstrates this scalability perfectly. By relying on more contractors than full-time employees, Google shifts resources across infrastructure management, development, and support functions as its operational needs change. Apart from megacorporations, SMBs also benefit from flexible scaling since it ensures consistent performance during peak demand while preventing unnecessary staffing costs.
Focus on Core Business Goals
Delegating IT operations to external providers allows companies to dedicate more time and resources to their primary objectives, such as product innovation, customer engagement, and market growth. When tasks like maintenance, troubleshooting, and software updates are handled externally, internal teams can focus on strategic initiatives that drive revenue and long-term competitiveness. Meta provides a relevant example, as it outsources content moderation and several IT-enabled processes to Accenture and other third-party firms, allowing internal teams to focus on core platform development, AI research, and user experience improvements.
Availability of Resources
Outsourcing ensures continuous access to the latest technologies, skilled personnel, and global support teams that operate around the clock, which is especially valuable for industries such as e-commerce, logistics, and healthcare services that rely on uninterrupted system performance. This constant availability helps businesses maintain stability during peak demand or unexpected disruptions. Many outsourcing firms operate across multiple time zones, providing 24/7 support and system monitoring to keep services running without interruptions. Such coverage reduces downtime, accelerates issue resolution, and strengthens overall business continuity.
Risks and Challenges of IT Outsourcing
Outsourcing presents several critical challenges that require careful management, ranging from minor communication barriers to hidden costs and critical data security issues. Identifying these risks early and implementing proper controls helps organizations maintain compliance, performance, and trust.
Data Security
Outsourcing increases the risk of data exposure significantly because sensitive information becomes accessible to external providers. Weak access controls, insecure storage practices, or improper handling of regulated data can lead to breaches, compliance violations, and substantial financial penalties. Industries that manage personal, financial, or health-related information are especially vulnerable, since mishandled data may violate GDPR, HIPAA, and regional privacy standards.
To address these concerns, organizations should require vendors to use encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring. Additionally, detailed data handling agreements, confidentiality clauses, routine security audits, and operating under a shared responsibility model help both parties maintain consistent security standards.
Communication and Time Zone Barriers
Collaborating with teams in different regions often leads to communication delays, slower decision-making, and misaligned expectations. Time zone gaps may limit overlapping work hours, making it difficult to resolve urgent issues or maintain project momentum. Language barriers, cultural differences, and inconsistent communication styles can further complicate collaboration, especially during fast-paced development cycles or real-time support operations. To strengthen coordination, businesses should establish overlapping work hours, assign liaison teams, and involve bilingual coordinators to bridge communication gaps. These steps help ensure that projects progress smoothly even when teams operate in different time zones.
Vendor Reliability
The reliability of an outsourcing partner determines service quality, continuity, and long-term performance. Vendors that lack stable processes, experienced staff, or the financial strength to support large workloads may cause service interruptions, delays, or inconsistent output. Poor reliability can also create bottlenecks in system maintenance, support response times, and software delivery, ultimately affecting overall business operations and customer satisfaction.
Organizations can reduce this risk by evaluating the vendor’s track record, client references, and service portfolio. Once the partnership begins, conducting review meetings and monitoring performance through predefined metrics and well-structured SLAs ensures further accountability.
Hidden Costs
Outsourcing can introduce unexpected expenses when agreements do not clearly define responsibilities, limitations, or long-term requirements. Hidden costs often arise in forms of onboarding, training, knowledge transfer, scope changes, system integrations, or post-contract support costs. They typically surface during transitions, major updates, or urgent tasks that fall outside the original agreement. To avoid these issues, businesses should document all pricing elements within the contract, including change request policies, onboarding fees, and support rates. Regular budget reviews, transparent billing, and a well-defined scope also preserve financial predictability when outsourcing.
When Should You Outsource IT Services?
Outsourcing IT services becomes the right choice when a business can no longer manage its technology requirements efficiently in-house due to limited expertise, rising costs, or growing operational demands. By shifting technical responsibilities to external providers, organizations can maintain smoother operations and access specialized skills without overextending internal teams. This approach is especially valuable for businesses that need reliable support, scalable resources, or advanced capabilities that are difficult or expensive to develop internally.
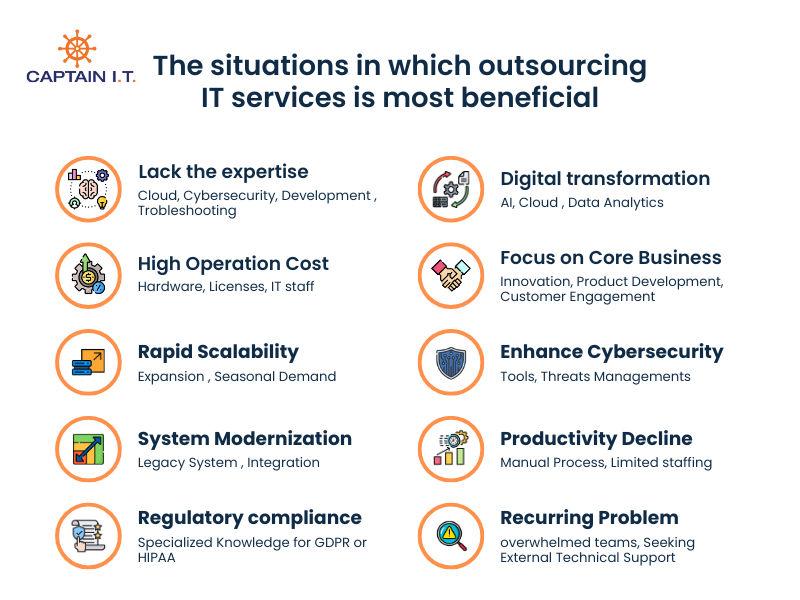
Following are the situations in which outsourcing IT services is most beneficial:
- Internal teams lack the expertise to manage technical tasks such as cloud deployment, cybersecurity, advanced software development, or complex troubleshooting.
- Operational tasks like maintaining hardware, software licenses, and IT staff become too costly to sustain internally.
- Companies need rapid scalability during expansion or seasonal spikes in demand, or face difficulty scaling their internal resources fast enough.
- Complex or legacy systems require modernization, integration, or maintenance that internal staff cannot handle efficiently.
- Strict compliance and security requirements, such as GDPR or HIPAA, require specialized knowledge that the team does not possess.
- Digital transformation initiatives demand advanced skills in automation, cloud migration, or data analytics which is too costly and difficult to maintain in-house.
- Leadership needs internal teams to focus on core operations like innovation, product development, and customer engagement rather than routine IT tasks.
- Cybersecurity concerns increase when in-house teams lack the tools or expertise to manage threats, making specialized vendors a safer alternative.
- Productivity declines when manual processes, limited staffing, or recurring technical issues slow down internal operations.
- Troubleshooting recurring system problems becomes overwhelming for internal teams, leading businesses to seek external technical support.
What Are the Common IT Outsourcing Pricing Models?
The common IT outsourcing pricing models are time and materials (T&M) pricing, fixed pricing, and performance-based pricing. Each model defines how services are billed, how risks and responsibilities are distributed, and how adaptable the arrangement remains throughout the contract. Organizations choose one of these models depending on factors like project complexity, desired cost predictability, and the required degree of oversight.
Time and Materials Pricing
Under the time and materials model, businesses are charged for the actual hours worked and resources used during the project, making it suitable for long-term or evolving projects where requirements change frequently. For instance, a company developing software that requires ongoing updates, feature additions, or iterative testing uses this model because it allows tasks and priorities to be adjusted as new needs emerge. This flexibility helps teams respond to changing scopes, but it also increases the risk of cost overruns if progress is not monitored closely. To maintain financial control, businesses must track work logs, review milestones regularly, and define boundaries for acceptable variations in scope.
Fixed Pricing
Companies looking for a predetermined cost for a defined set of deliverables choose fixed pricing because it provides clarity on scope, timeline, and total budget from the beginning. This works well for stable projects like app development, planned system migrations, or network upgrades. For example, a business implementing a new inventory management system selects fixed pricing because all features and integration steps are known in advance. With all details documented upfront, this structure offers strong financial predictability and shifts responsibility to the vendor to deliver within the agreed timeframe. Its main drawback is limited flexibility, since any change in scope requires contract adjustments or added fees, making accurate planning crucial.
Performance-Based Pricing
Performance-based pricing links payments directly to measurable outcomes such as system uptime, response times, or milestone achievements, rather than hours or fixed costs. This model motivates MSPs to focus on results that align with business objectives, whether improving service availability or accelerating project delivery. For example, a service provider might earn additional compensation for maintaining 99.9% uptime or surpassing efficiency benchmarks. While this structure promotes accountability and high-quality performance, its success depends on clearly defined metrics, accurate tracking systems, and agreement on what counts as acceptable results. Without well-structured KPIs, performance-based contracts may lead to disputes or unmet expectations.
Best Practices for Successful IT Outsourcing
For successful IT outsourcing, businesses must set clear expectations and scope, communicate regularly, monitor performance, build a collaborative relationship with the vendor, and plan for knowledge transfer. Applying these practices strengthens coordination, minimizes risks, and ensures that vendor performance aligns with business objectives.
Establish Clear Expectations and Scope
Defining project goals, deliverables, and timelines at the start prevents confusion and scope creep later in the process. Both parties should agree on detailed service requirements, measurable outcomes, and success criteria. A well-written contract should outline the scope, budget, and escalation process to resolve issues efficiently. This clarity builds accountability and provides a foundation for tracking progress throughout the project.
Maintain Regular Communication
Consistent communication between the business and the outsourcing partner strengthens alignment and reduces potential misunderstandings. Scheduled meetings, status updates, and shared project dashboards create transparency and encourage collaboration. Using tools such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, or project management platforms helps keep discussions centralized and traceable. Frequent interaction ensures issues are addressed promptly and project objectives stay on track.
Monitor Performance with KPIs
Tracking vendor performance through measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) ensures accountability and service quality. Metrics such as response time, system uptime, and issue resolution rates provide insight into operational effectiveness. Regular reviews of these metrics allow businesses to identify improvement areas and maintain consistent standards. This data-driven approach ensures that outsourcing partners meet the expected performance benchmarks and deliver ongoing value.
Build Collaborative Relationships
A strong working relationship fosters mutual trust and better problem-solving between the organization and its vendor. When vendors are treated as strategic collaborators rather than external contractors, communication improves, feedback loops are created, and objectives remain aligned. Collaborative partnerships promote flexibility, strengthen team morale, and contribute to higher project success rates. Maintaining professionalism and mutual respect is essential for sustaining these long-term relationships.
Plan for Knowledge Transfer
Documenting and sharing operational knowledge ensures that critical information is not lost during staff transitions or contract changes. Businesses should establish structured handover processes, maintain centralized documentation repositories, and conduct periodic training sessions to keep both internal and external teams aligned. Involving in-house staff in key project stages helps preserve institutional knowledge and operational consistency. Structured knowledge transfer supports continuity and reduces dependency on any single provider.
What Legal and Contractual Considerations Should You Know?
Businesses must ensure contracts clearly define performance expectations through Service Level Agreements (SLAs), protect sensitive information under Data Protection and Privacy clauses, and establish ownership rights with clear Intellectual Property (IP) terms. These foundational elements safeguard both parties, promote accountability, and prevent disputes throughout the engagement. The main legal and contractual areas to consider include:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
- Data Protection and Privacy
- Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
- Termination and Exit Clauses
- Dispute Resolution and Jurisdiction
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
An SLA outlines the quality and performance standards the vendor must meet. It specifies measurable metrics such as uptime percentages, response times, and escalation procedures. For example, a managed service provider might be required to maintain 99.9 percent system uptime or respond to critical incidents within one hour. Clear SLAs ensure that both parties have defined expectations and mechanisms for accountability. Regular performance reviews and penalty clauses for underperformance further reinforce service reliability and trust.
Data Protection and Privacy
Safeguarding sensitive business and customer data is a legal necessity in any outsourcing relationship. Vendors handling information must comply with data protection laws such as GDPR, CCPA, or HIPAA, depending on jurisdiction. Contracts should define how data is collected, processed, stored, and shared, as well as the security measures in place to prevent unauthorized access. Businesses must verify that the vendor follows encryption standards, access controls, and regular security audits to ensure compliance and reduce liability.
Intellectual Property (IP) Rights
Ownership of software, designs, and other intellectual assets developed during an outsourcing project must be explicitly defined. The contract should specify which party holds IP rights upon project completion and include clauses addressing confidentiality and licensing terms. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are essential to prevent unauthorized use or distribution of proprietary information. Clearly defining IP ownership protects the company’s innovations and minimizes the risk of disputes later on.
Termination and Exit Clauses
Termination clauses provide guidance on how either party can end the contract without legal or operational complications. They outline notice periods, exit timelines, and obligations such as data return, asset transfer, or final payments. For example, if a company decides to switch IT service providers after a contract term, a clear exit plan ensures secure data transfer and uninterrupted operations. Including post-termination support allows both parties to complete the transition smoothly and maintain business continuity during the changeover.
Dispute Resolution and Jurisdiction
Disagreements can occur even in well-managed outsourcing partnerships, which makes predefined resolution mechanisms essential. Contracts should clearly state how conflicts will be addressed, whether through mediation, arbitration, or formal legal proceedings, and must specify the applicable governing law and jurisdiction. Defining these terms in advance helps reduce both time and cost if disputes arise. Transparent communication and fair negotiation further support resolution before issues escalate.
What Does the Future Hold for IT Outsourcing?
The IT outsourcing industry is evolving rapidly as automation, AI, cloud computing, and remote collaboration reshape how organizations manage technology. These changes are shifting outsourcing from a cost-saving measure to an innovation-focused partnership that creates smarter, faster, and more cost-efficient service delivery.
Key trends shaping the future of IT outsourcing include:
- Automation and AI Integration: Intelligent systems are streamlining repetitive processes such as monitoring, maintenance, and analytics, reducing manual effort while improving accuracy.
- Cloud-Driven Infrastructure: Scalable cloud platforms enable seamless deployment, data storage, and remote collaboration, helping businesses adapt quickly to fluctuating demands.
- Growth of Remote Work: Distributed teams have made outsourcing more flexible, allowing companies to access skilled professionals globally without geographic constraints.
- Focus on Cybersecurity: As digital operations expand, vendors are investing in advanced security frameworks to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
- Outcome-Based Partnerships: Clients increasingly prefer performance-based models that link vendor compensation to measurable business results.
How to Choose the Right IT Outsourcing Partner?
When selecting an IT outsourcing partner, organizations should evaluate reliability, technical expertise, communication quality, and alignment with business goals. The right provider ensures consistent performance, strong security, and transparent pricing, leading to a partnership that drives efficiency, scalability, and measurable results. Key factors to consider when choosing an IT outsourcing partner include:
- Vendor Reputation and Experience: Assess the provider’s reviews, case studies, and certifications to confirm reliability and proven results.
- Security and Compliance Practices: Ensure robust security protocols and adherence to GDPR, ISO 27001, or SOC 2 standards for data protection.
- Technical Expertise and Capabilities: Evaluate the provider’s tools, skills, and ability to support future needs like cloud migration or automation.
- Transparent Pricing Models: Look for detailed cost structures and breakdowns whether under fixed, time-based, or performance-linked models.
- Communication and Collaboration: Evaluate how they manage coordination, progress reporting, response times, and communication.
- Defined Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Confirm that measurable KPIs, timelines, and escalation steps are clearly stated on the contract.
A strong outsourcing partnership is built on trust, competence, and shared objectives. By evaluating vendors carefully and defining expectations early, businesses can secure a reliable IT service provider that enhances efficiency, drives innovation, and supports sustained growth.