What Is IT Support?
IT support is the service that provides technical assistance and system maintenance to end users, customers, and businesses, ensuring their technology functions reliably and securely. It focuses on helping individuals access and use computers, software, networks, and digital services without disruption, while also maintaining the underlying systems that support those activities.
In practice, IT support assists end users and customers by troubleshooting technical problems, restoring access, maintaining devices, and protecting data. IT support services are delivered through various service models, including help desk, on-site, remote, managed IT, network, and cloud computing support. These services are further organized into structured support levels so that basic issues are handled efficiently while complex or critical problems are escalated to specialized expertise.
IT support also addresses common user-facing issues, including connectivity failures, forgotten passwords, printing errors, software installation problems, hardware malfunctions, slow performance, and data loss. By resolving these problems promptly and applying preventive measures such as monitoring, updates, and security controls, IT support improves productivity, enhances cybersecurity, reduces downtime, and ensures consistent access to essential digital services for both users and customers.
What Does IT Support Do?
IT support provides technical assistance and system management services that help end users, customers, and businesses keep their technology operational, secure, and accessible. Its role is to ensure people can reliably use computers, applications, networks, and digital platforms without disruption, whether they are internal employees or external customers accessing services.
Rather than focusing only on fixing problems, IT support combines immediate issue resolution with ongoing maintenance and preventive oversight. It handles access failures, connectivity issues, and application errors while maintaining infrastructure, monitoring system performance, and reducing the risk of repeat disruptions. This work follows a structured flow that helps maintain availability, protect systems and data, and restore services quickly when incidents occur.
Core Functions of IT Support are:
- Maintaining system uptime: Ensuring that computers, servers, networks, and applications remain available and functional during business operations.
- Deploying and maintaining cybersecurity controls: Implementing security measures to protect systems from malware, unauthorized access, and evolving cyber threats.
- Enabling secure remote and on-site access: Supporting employees in accessing systems from offices, remote locations, or mobile environments without compromising security.
- Installing and configuring hardware and software: Setting up computers, operating systems, applications, networks, printers, and peripheral devices for end users.
- Managing servers and scheduled maintenance: Performing routine updates, patches, and planned maintenance to maintain system stability and performance.
- Maintaining and repairing computers and devices: Troubleshooting hardware faults, replacing components, and resolving physical device issues.
- Resolving access and authentication issues: Assisting users with forgotten passwords, account lockouts, and permission-related problems.
- Protecting and restoring data: Managing backups and recovering deleted or lost files following system failures, cyber incidents, or accidental data loss.
- Logging, tracking, and supporting IT requests: Recording incidents and service requests to ensure issues are addressed consistently and escalated appropriately when needed.
What are the Different Types of IT Support Services?
The main types of IT support services include help desk support, on-site IT support, managed IT services, remote IT support, network support, and cloud computing support. These service models define how technical assistance is delivered to users and systems, with each type focusing on a specific method of support or area of responsibility.
Businesses and service providers often use a combination of these IT support services based on user needs, system complexity, service availability requirements, and the environments in which customers or employees access technology. Together, these service types ensure that technical issues can be addressed efficiently across different devices, platforms, locations, and delivery modes.
Help Desk Support
Help desk support is an IT support service that provides a centralized point of contact for end users to report technical issues related to day-to-day system use. It primarily handles user-facing problems such as login failures, basic software errors, access requests, and routine connectivity issues.
Within the overall IT support framework, help desk support plays an intake and triage role that structures how incidents enter the resolution process. It ensures that issues are properly logged, categorized, and resolved when possible, while unresolved problems are referred to higher-level IT support teams for further investigation.
On-Site Support
On-site IT support is a form of IT support service that delivers in-person technical assistance when issues require physical access to equipment or infrastructure. It is commonly used for hardware failures, device installations, cabling issues, and physical network or system changes.
As part of IT support services, on-site support addresses problems that cannot be resolved remotely. This hands-on role enables technicians to inspect systems directly, replace components, and restore functionality in environments that require physical presence.
Managed IT Services
Managed IT services are an IT support service model that provides continuous, proactive management of an organization’s IT environment. This approach focuses on maintaining system stability through monitoring, maintenance, updates, and preventive issue management rather than reacting only after problems occur.
Instead of functioning as ad hoc technical support, managed IT services consolidate oversight, maintenance, and issue resolution into a structured, ongoing partnership. This model unifies multiple IT responsibilities under a consistent service framework that supports long-term operational stability and predictable performance.
Remote IT Support
Remote IT support is an IT support service that provides technical assistance through secure remote access to systems and devices. It is commonly used to resolve software issues, configuration problems, performance concerns, and user access errors without requiring on-site intervention.
Because technicians can connect directly to systems from any location, remote IT support removes geographic barriers from service delivery. This approach shortens response times, accelerates troubleshooting, and reduces the downtime and scheduling delays associated with on-site visits.
Network Support
Network support is a specialized IT support service focused on maintaining the reliability, performance, and security of an organization’s network infrastructure. This includes managing local area networks, internet connectivity, routing devices, and wireless access systems.
Because all systems depend on stable connectivity, this service underpins many other IT support functions. Network support addresses disruptions, performance limitations, and configuration issues that can affect multiple users and systems simultaneously.
Cloud Computing Support
Cloud computing support is an IT support service that manages and maintains cloud-based systems, applications, and data environments used by end users and customers. It focuses on ensuring reliable access, correct configuration, secure authentication, and stable performance of cloud-hosted resources across different devices and locations.
As businesses and service providers increasingly rely on cloud platforms to deliver digital services, this form of IT support ensures consistent availability and operational continuity for users and customers. Cloud computing support helps ensure alignment among cloud services, on-premises systems, and user access requirements, so that individuals can securely access applications and data without disruption.
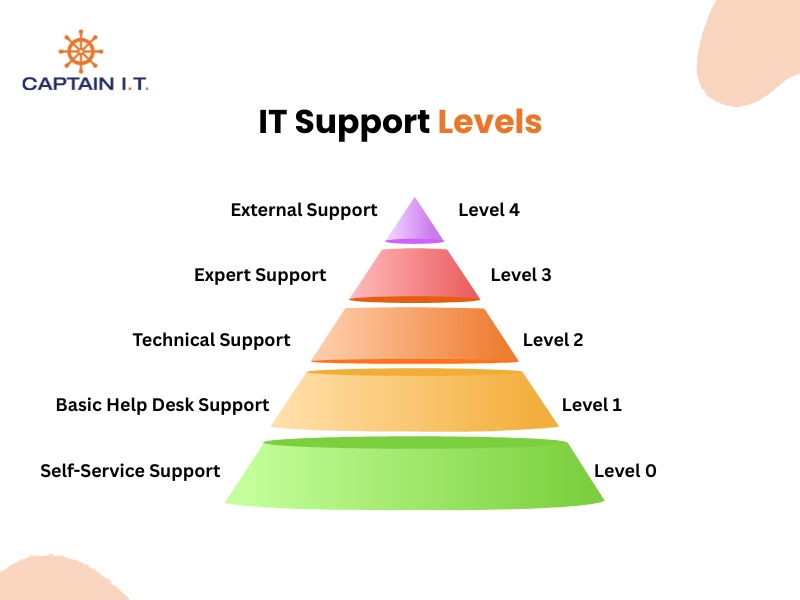
What Are the Different Levels of IT Support?
The types of IT support are organized into defined support levels, commonly referred to as Level 0, Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, and Level 4, which classify technical issues based on complexity, impact, and escalation requirements. Within structured IT service environments, IT support levels define the scope of responsibility, technical depth, and escalation authority required to resolve specific categories of incidents. This layered model ensures that simple user requests are handled efficiently while complex system-level disruptions are directed to advanced technical specialists.
- Level 0 IT Support – Self-Service Support
Level 0 IT support provides self-service resources that allow users to resolve basic technical issues without direct IT staff involvement. It serves as the first line of defense against common, repetitive problems by enabling users to find answers and complete simple tasks independently, without direct human interaction.
Also known as Self-Service Support, Level 0 includes resources such as FAQs, knowledge base articles, step-by-step guides, and instructional documentation. These resources help users handle routine issues such as account setup questions, basic configuration tasks, and password-related problems without submitting a support request.
In many organizations, Level 0 IT support is supported by chatbots, virtual assistants, and AI-powered search tools that provide real-time guidance. By resolving straightforward issues at the user level, this support tier reduces demand on higher levels of IT support and allows technical staff to focus on more complex and impactful problems.
- Level 1 – Basic Help Desk Support
Level 1 IT support provides direct assistance to users by handling basic technical issues that require human interaction and initial troubleshooting. It serves as the first point of human contact when self-service resources cannot resolve a problem.
This frontline support level is responsible for resolving most routine user issues, typically handling around 70–80% of reported problems. Level 1 support staff use standard support tools, such as ticketing systems and knowledge bases, to address issues, including login errors, application access problems, basic software faults, and connectivity issues. Issues that cannot be resolved at this level are documented and escalated to Level 2.
By resolving common problems quickly, Level 1 IT support helps maintain daily productivity and ensures consistent handling of user requests. It also plays a key role in accurately classifying issues and passing unresolved cases to higher support levels with the necessary context.
- Level 2 – Technical Support
Level 2 IT support provides advanced technical assistance for issues that cannot be resolved through basic troubleshooting or standard procedures. This level handles problems that require deeper technical knowledge and more detailed analysis than what is available at Level 1.
Level 2 support typically addresses recurring system errors, complex software issues, hardware faults, and network-related problems that affect functionality beyond a single user. Support staff at this level perform in-depth diagnostics, analyze system logs, and identify underlying causes within existing system configurations rather than applying predefined fixes. Issues are investigated more thoroughly to determine why they occurred and how to correct them.
By resolving more complex issues and identifying root causes, Level 2 IT support helps reduce repeat incidents and stabilizes systems over time. When a problem exceeds their scope or requires specialized expertise, it is escalated to higher support levels (Levels 3 and 4), along with detailed findings and technical context.
- Level 3 – Expert Support
Level 3 IT support provides expert-level technical assistance for complex issues that cannot be resolved at lower support levels. This level handles problems that significantly impact systems, infrastructure, or core business operations and require specialized technical expertise.
At this level, IT support focuses on resolving issues that originate from deeper system design, configuration, or software behavior and may require changes to system architecture or core configurations rather than surface-level faults. Level 3 support addresses advanced system failures, complex software defects, critical infrastructure issues, and problems that require in-depth engineering knowledge. IT support specialists analyze system architecture, apply advanced fixes, and implement corrective changes to restore stability across affected environments.
Beyond incident resolution, Level 3 IT support contributes to long-term system reliability by identifying structural weaknesses and preventing future failures. When an issue requires product-specific intervention or external expertise beyond internal capabilities, it is escalated to the next support level (Level 4) and accompanied by comprehensive technical documentation.
- Level 4 – External Support
Level 4 IT support involves external support provided by software vendors or hardware manufacturers when an issue cannot be resolved internally. This IT support level is used for product-specific problems that fall outside an organization’s internal IT support capabilities and require vendor-authorized intervention.
Engagement at Level 4 occurs when resolution depends on vendor-controlled processes, contractual obligations, or specialized product knowledge. IT support works with external providers under defined service-level agreements (SLAs) that govern response times, resolution expectations, and support responsibilities. These cases often involve warranties, proprietary software issues, firmware defects, or specialized hardware failures that require authorized vendor intervention.
Level 4 IT support ensures that highly specialized problems are addressed by the original product providers while internal IT support manages coordination and oversight. After the vendor resolves the issue, internal IT support validates system stability, restores normal operations, and documents the outcome to support future incident handling.
Why Is It Important to Have Multiple IT Support Levels?
Multiple IT support levels are important to efficiently handle technical issues based on their complexity, urgency, and impact on end users and customers. A tiered IT support structure allows routine and high-volume user problems to be resolved quickly at lower levels, while more complex or critical issues are escalated to specialists with the appropriate technical expertise.
By organizing IT support into defined levels, service providers improve response times, reduce unnecessary escalation, and ensure consistent handling of technical issues affecting users and customers. This structured approach supports accountability, helps prevent recurring problems through proper documentation and root-cause analysis, and allows IT support services to scale effectively as user demand, system complexity, and service requirements grow.
What Are the Most Common IT Support Issues?
The most common IT support issues include connectivity and slow internet problems, printing failures, forgotten passwords, software installation errors, hardware malfunctions, email disruptions, slow system performance, overheating devices, and accidental data loss. These issues arise during daily business operations and can disrupt user productivity if not resolved promptly through structured IT support processes.
Below are the 10 most common IT support issues and the methods IT support uses to resolve them.
- Connectivity issues:
IT support resolves connectivity problems by diagnosing network configurations, testing network paths, and restoring access by adjusting router, switch, or wireless settings. Monitoring tools and network diagnostics are used to identify interruptions and stabilize connections.
- Printing problems:
IT support fixes printing issues by checking device connectivity, reinstalling or updating printer drivers, clearing print queues, and resolving configuration conflicts between printers and user systems.
- Installing software:
IT support handles software installation problems by deploying applications through approved installation methods, resolving compatibility issues, applying updates, and ensuring correct system permissions.
- Swapping out hardware:
IT support replaces faulty hardware by diagnosing component failures, installing replacement devices, transferring configurations or data, and validating system functionality after the swap.
- Email issues:
IT support resolves email problems by checking server availability, correcting configuration settings, restoring mailbox access, and validating email flow using email management and diagnostic tools.
- Forgotten Passwords:
IT support restores access by verifying user identity, resetting credentials, unlocking accounts, and enforcing authentication policies through access and identity management systems.
- Accidentally Deleted Important Files:
IT support recovers deleted files by restoring data from backups, repairing storage errors, or retrieving previous file versions using backup and recovery tools.
- Slow Performance:
IT support improves system performance by identifying resource constraints, removing conflicting processes, applying system updates, and optimizing configurations using performance monitoring tools.
- Overheating:
IT support addresses overheating by inspecting hardware conditions, improving airflow or cooling, updating firmware, and resolving issues that cause excessive system load or instability.
- Slow Internet Connection:
IT support resolves slow internet issues by testing bandwidth, identifying network congestion, correcting configuration errors, and coordinating with service providers when external connectivity is affected.
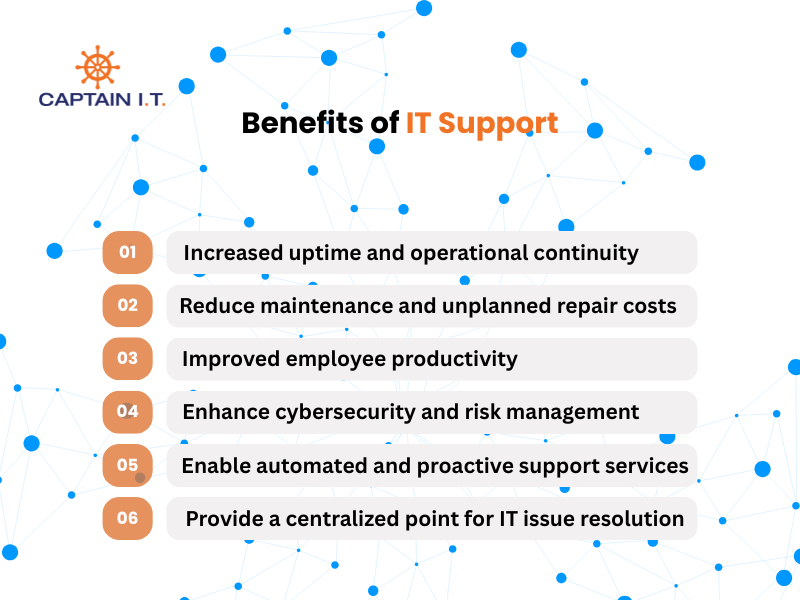
How Can IT Support Benefit Your Business?
IT support benefits a business by increasing system uptime, reducing maintenance costs, improving employee productivity, strengthening cybersecurity, enabling proactive support, and providing a centralized way to manage IT issues. These outcomes represent measurable IT support benefits that directly affect operational continuity, cost stability, and system reliability in technology-dependent environments. Through structured support processes and ongoing system management, IT support reduces disruptions, stabilizes infrastructure, and ensures technology remains available for daily operations.
The following benefits explain how IT support creates these outcomes in practice.
- Increases uptime and operational continuity
IT support increases uptime by continuously monitoring systems and responding to technical issues before they escalate into outages. When failures occur, structured incident-handling and escalation processes enable IT support teams to restore affected services and minimize operational disruption quickly.
- Reduces maintenance and unplanned repair costs
IT support reduces maintenance and repair costs by identifying potential system issues before they develop into critical failures. Preventive maintenance practices, such as regular updates, system checks, and early fault detection, help prevent expensive emergency repairs and unplanned hardware or software replacements.
- Improves employee productivity
IT support improves employee productivity by ensuring reliable access to systems, applications, and data required for daily work. When technical issues arise, timely troubleshooting and resolution reduce downtime and prevent prolonged interruptions that slow individual and team output.
- Enhances cybersecurity and risk management
IT support enhances cybersecurity by actively reducing exposure to vulnerabilities and limiting the impact of security incidents. This is achieved through patch management, access control enforcement, system monitoring, and structured response procedures that protect systems and sensitive data.
- Enables automated and proactive support services
IT support enables proactive service delivery by identifying technical issues before users are affected through automated monitoring and alerting processes. Routine tasks and recurring problems are handled consistently, reducing reliance on reactive support and improving overall system stability.
- Provides a centralized point for IT issue resolution
IT support provides centralized issue resolution by serving as a single point of coordination for reporting, tracking, and managing technical problems. This approach ensures issues are documented properly, addressed consistently, and escalated efficiently across the organization.
What Are the Different Job Roles in IT Support?
IT support services are delivered by IT Support Technicians, IT Support Specialists, and Help Desk Technicians, each with defined technical responsibilities for system maintenance, issue resolution, and user assistance. These roles work together within the IT support structure to ensure that technical problems are handled at the appropriate level and that day-to-day operations remain stable.
IT Support Technician
An IT Support Technician provides hands-on IT support by maintaining end-user devices and resolving hardware-related issues that affect daily operations. This role focuses on physical and device-level support to keep computers, printers, mobile devices, and peripherals functioning reliably across the organization.
IT Support Technicians handle tasks such as imaging and deploying workstations, installing and replacing internal components, configuring peripherals, and performing routine maintenance. They diagnose hardware faults using standard testing methods, apply firmware or operating system updates, and ensure devices meet baseline configuration standards. Through proactive checks and timely repairs, their work reduces downtime from equipment failures and ensures consistent access to end-user technology.
IT Support Specialist
An IT Support Specialist provides advanced IT support by resolving complex technical issues that require strong system knowledge and analytical troubleshooting skills. This role focuses on service stability by addressing problems that persist beyond basic troubleshooting or standard support procedures.
IT Support Specialists investigate software behavior issues, system configuration conflicts, performance degradation, and recurring incidents across operating systems and applications. They analyze logs, trace root causes, and implement corrective actions such as configuration changes, patches, or process improvements. By documenting findings and contributing to long-term fixes, they help reduce repeat incidents and strengthen system reliability across the environment.
Help Desk Technician
A Help Desk Technician supports IT support services by acting as the primary point of contact for user-reported technical issues. This role ensures that users receive prompt assistance while maintaining accurate records of incidents and service requests.
Help Desk Technicians log requests through ticketing systems, gather relevant information, and perform initial troubleshooting using established procedures. They resolve common issues such as password resets, account access problems, basic software errors, and connectivity concerns. When problems require deeper investigation, they escalate tickets with clear documentation and diagnostic details to support efficient resolution by higher-level IT teams.
What Skills and Certifications Are Required for IT Support Roles?
IT support services rely on a combination of problem-solving skills, technical knowledge, effective communication, and recognized certifications to deliver consistent, reliable support. These capabilities, supported by formal certifications, ensure that IT support teams can accurately diagnose issues, resolve them efficiently, and clearly communicate solutions to users.
The key skill and qualification areas that support IT support service delivery include:
- Core technical (hard) skill
Technical skills include knowledge of computer systems, operating systems, networks, and structured troubleshooting methods. These skills allow IT support teams to identify faults, resolve hardware and software issues, and restore system functionality across different environments.
- Communication and problem-solving (soft) skills
Soft skills such as clear communication, customer service, and analytical problem-solving are essential for gathering accurate information, documenting incidents, and guiding users through resolutions. These skills help ensure issues are handled efficiently and consistently within IT support processes.
- Certification and service management certifications
Certifications such as CompTIA A+, ITIL, and Microsoft certifications are commonly used to validate technical knowledge and service management practices. These qualifications help standardize IT support procedures, reinforce best practices, and support consistent service delivery without defining individual career pathways.
What Are the Differences Between In-House and Outsourced IT Support?
In-house IT support is delivered by internal employees who manage technology systems within the organization, whereas outsourced IT support is provided by an external service provider (MSP) under defined service agreements. Both models support system reliability and issue resolution, but they differ in control, cost, and scalability.
In-house IT support offers direct control and tailored support through teams that understand internal systems and workflows. This familiarity supports faster responses and closer alignment with business needs, though it often involves higher staffing and operational costs.
In contrast, outsourced IT support provides a more flexible and cost-efficient option, offering scalable support and access to specialized expertise. While it reduces internal overhead, service delivery is guided by contractual agreements rather than direct internal control.
Which IT Support Option Is Right for Your Business?
The right IT support option depends on factors such as business size, technical complexity, budget constraints, and operational priorities. Organizations with stable environments and specific internal requirements may benefit from in-house IT support, where teams have direct familiarity with internal systems and workflows.
The table below provides clear guidance in selecting the right IT support option for your business:
| Decision Factor | In-House IT Support | Outsourced IT Support |
| Business Size | Medium to large organizations with consistent support needs and dedicated internal users | Small to mid-sized organizations without enough demand to justify a full internal team |
| Technical Complexity | Stable, well-defined environments with known systems, applications, and internal workflows | Mixed or changing environments with diverse technologies or evolving infrastructure requiring broader expertise |
| System Familiarity | High familiarity with internal systems, business processes, and organizational priorities | Knowledge based on documentation and service agreements |
| Scalability | Requires hiring, training, and long-term staffing commitments | Scales on demand without internal staffing changes |
| Cost Structure | Fixed costs related to salaries, training, tools, and benefits | Subscription or usage-based costs |
| Availability | costs related to salaries, training, tools, and benefits | Extended or after-hours and 24/7 on-call support, depending on the service model |
| Operational Control | Full internal control over priorities, workflows, and support processes | Governed by service level agreements (SLAs) |
What Tools and Technologies Are Used in IT Support?
IT support relies on ticketing systems, remote access tools, monitoring platforms, cybersecurity solutions, and system management technologies to manage incidents, secure environments, and resolve technical issues efficiently. These tools help IT support teams standardize workflows, reduce response times, and deliver consistent support across users, devices, and systems.
The following categories represent the core tools used in IT support services and explain how each supports efficient operations and improved productivity.
- Ticketing systems:
Ticketing systems are used to log, track, prioritize, and manage IT support requests from initial reporting through resolution. Platforms from providers such as ServiceNow, Atlassian (Jira Service Management), and Zendesk improve productivity by ensuring that issues are documented, correctly assigned, and escalated in a structured manner, reducing missed requests and duplication of effort.
- Remote access and remote desktop tools:
Remote access tools allow IT support teams to securely connect to user systems without being physically present. Solutions such as TeamViewer, AnyDesk, and Microsoft Remote Desktop enable faster troubleshooting, configuration changes, and issue resolution, reducing downtime and eliminating delays associated with on-site support.
- System and network monitoring tools:
Monitoring tools track system health, performance, and network activity in real time. IT support teams use tools such as Nagios, SolarWinds, and PRTG to identify performance bottlenecks, detect failures early, and respond to issues before they affect users, improving system stability and uptime.
- Cybersecurity and endpoint protection tools:
Security tools help IT support teams protect systems against malware, unauthorized access, and known vulnerabilities. Platforms such as Microsoft Defender, CrowdStrike, and Sophos support patch management, access control, and threat detection, helping IT support teams reduce security risks while maintaining system integrity.
- System management and configuration tools:
System management tools are used to deploy updates, enforce configurations, and maintain consistency across devices. Solutions such as Microsoft Intune and Configuration Manager support automated patching, device compliance, and centralized system administration, reducing manual maintenance effort.
How Is IT Support Evolving with Technology?
IT support is shifting from reactive issue resolution to proactive and predictive operations through automation, artificial intelligence, and security-driven design. Automation now manages routine tasks such as system health checks, patch deployment, access provisioning, and configuration enforcement, reducing manual effort and maintaining consistent standards. Autonomous Self-Healing Systems extend this capability by detecting known issues and automatically applying corrective actions, often resolving problems before users are impacted.
Artificial intelligence extends this shift through AI-driven chatbots, virtual support agents, generative AI, and AIOps platforms. These tools guide users through common fixes, analyze system logs and performance data, and prioritize incidents based on business impact. Intelligent monitoring uses pattern recognition and predictive analysis to flag potential failures early, while Zero-Trust Models (ZTM) enforce continuous access validation. Together, automation and AI allow IT support teams to focus on complex issues while delivering faster, more reliable support at scale.
How Can You Measure the Effectiveness of IT Support?
You can measure the effectiveness of IT Support using response time, resolution time, first-contact resolution rate, system availability, incident recurrence, and user satisfaction. These performance indicators help organizations determine how efficiently issues are handled, how reliable systems remain, and how well IT support services meet operational expectations.
The following metrics and methods are commonly used to evaluate IT support effectiveness:
- Response time:
Measures how quickly IT support acknowledges and begins working on reported issues. Faster response times reflect efficient intake, prioritization, and workload management.
- Resolution time:
Tracks the total time required to fully resolve technical issues. Shorter resolution times indicate effective troubleshooting, escalation paths, and coordination across support levels.
- First-contact resolution rate:
Indicates the percentage of issues resolved during the initial interaction without escalation. Higher rates suggest strong frontline expertise and well-defined support procedures.
- System availability and uptime:
Evaluates how consistently systems and services remain operational. High availability points to proactive monitoring, preventive maintenance, and effective incident response.
- Incident recurrence rate:
Measures how often previously resolved issues reappear. Lower recurrence rates reflect successful root-cause analysis and lasting corrective actions.
- User satisfaction and feedback:
Assesses user experience through surveys, ratings, or direct feedback. Positive results indicate clear communication, timely resolution, and dependable support interactions.
How Does IT Support Align with Your Business Strategy?
IT support aligns with business strategy by ensuring that technology systems reliably support operational goals, growth plans, and risk management requirements through effective IT service management (ITSM). By maintaining system availability, minimizing disruptions, and enabling secure access to tools and data, IT support stabilizes day-to-day operations, ensuring IT services are delivered in a structured, measurable, and repeatable manner. This alignment helps organizations integrate technology into broader business objectives and long-term growth strategies rather than treating IT as a standalone function.
Key ways IT support aligns with business strategy include:
- Maintaining system uptime and performance to support core operations
- Reducing downtime that impacts productivity and customer experience
- Supporting scalable technology adoption aligned with growth strategies
- Enforcing security controls and access management to reduce operational and compliance risk
- Standardizing systems and processes to improve efficiency
- Enabling compliance with regulatory and internal governance requirements
How to Choose the Right IT Support Solution for Your Business?
Choosing the right IT support solution involves aligning support services with how your organization uses technology, the complexity of your systems, and the level of reliability required to maintain operations. The objective is to ensure technical issues are resolved efficiently while avoiding unnecessary cost or resource strain.
Key factors to consider when selecting an IT support solution include:
- Business size and structure, including distributed teams or multiple locations
- System complexity and reliance on critical applications or infrastructure
- Frequency, timing, and impact of technical issues
- Required response times and acceptable downtime levels
- Scalability to support growth, new technologies, or expansion
- Support coverage, including hours of service and escalation paths
- Service management processes and performance measurement methods
By evaluating these factors, organizations can determine the level of support they require and select a model that aligns with daily operations. When internal resources are limited, working with a managed service provider provides structured support and scalable coverage. This approach ensures system reliability while supporting future growth.
What Are the Future Trends in IT Support Services?
Future trends in IT support focus on improving efficiency, reducing reactive workloads, and strengthening system reliability as technology environments become more complex and distributed. IT support is evolving from traditional issue resolution toward proactive, intelligence-driven service models that integrate automation, security, and resilience into daily operations.
Key future trends shaping IT support include:
- Adoption of AIOps to analyze system data, correlate events, and predict incidents before they impact users
- Use of AI-guided portals and virtual support agents to support self-service and guided troubleshooting
- Expanded use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to automate repetitive support and maintenance tasks
- Growth of remote and cloud-based support models to enable Hybrid Work Optimization
- Stronger integration of cybersecurity into IT support through Security Operations (SecOps), continuous monitoring, and faster incident response
- Broader application of Enterprise Service Management (ESM) to standardize service delivery across business functions
- Increased emphasis on Green IT and Sustainability through efficient resource usage and reduced environmental impact