Managed endpoint security is a service-driven cybersecurity approach that protects endpoint devices such as laptops, servers, and mobile systems through continuous monitoring, advanced threat detection, and expert-led response. It operates by deploying lightweight endpoint agents connected to centralized cloud platforms, where endpoint activity is analyzed in real time using behavioral analysis, threat intelligence, and machine learning. This model enables rapid detection, automated containment, and ongoing improvement of security controls, thereby reducing the risk that threats will escalate into business-disrupting incidents.
By combining multiple security capabilities such as endpoint protection platforms (EPP), endpoint detection and response (EDR), unified endpoint management (UEM), cloud-based security, and AI-powered analytics, managed endpoint security delivers layered defense and centralized visibility. Supported by 24/7 SOC monitoring and managed by MSPs, it helps organizations of all sizes, especially SMBs, reduce security workload, strengthen compliance, accelerate incident response, and maintain a resilient endpoint security posture without relying on in-house security teams.
How Does Managed Endpoint Security Work?
Managed endpoint security works through a centralized, continuous workflow that connects lightweight agents on endpoint devices such as laptops, servers, and mobile devices to a provider’s cloud analytics platform. These agents monitor system behavior through AI, collect telemetry such as process activity and network events, and enforce security policies in real time, ensuring ongoing visibility and control across all endpoints.
Key aspects of how managed endpoint security works:
- Agent Deployment and Monitoring
Lightweight endpoint agents are deployed across all endpoint devices to continuously monitor system activity. These agents collect telemetry including disk I/O, process execution, and network requests, allowing security teams to maintain visibility into endpoint behavior without disrupting daily operations. - Centralized Control
Telemetry from all endpoints is aggregated into a centralized management console or cloud platform. This centralized view enables IT teams to manage security policies, review alerts, and oversee endpoint security from a single control point, improving operational efficiency and consistency. - Threat Detection and Prevention
The platform analyzes endpoint activity using behavioral analysis, artificial intelligence, and automated detection logic. By evaluating patterns and deviations from normal behavior, it identifies suspicious activity such as malware execution or unauthorized access in real time. - Incident Analysis and Response
Once a threat is identified, automated containment actions are initiated, including endpoint isolation or process termination. Security analysts then investigate alerts, validate incidents, and coordinate remediation efforts to prevent lateral movement and further impact. - Proactive Maintenance
Continuous patch and vulnerability management ensures endpoints remain up to date. Insights gathered from telemetry and incident investigations are used to refine detection logic and update security controls, strengthening endpoint protection over time.
What Are the Key Components of Managed Endpoint Security?
The key components of managed endpoint security include the endpoint security agent, centralized management console, threat detection, automated incident response, security patches, threat intelligence integration, and human-led SOC monitoring. Each component performs a specific role, and their integration enables centralized control, real-time threat detection, and coordinated incident response for businesses of every scale, from SMBs to larger enterprises.

Key components of managed endpoint security are:
- Endpoint security agent: Installed on each endpoint device, the security agent actively runs in the background to collect telemetry such as process execution, file changes, and network behavior. It captures events in real time and forwards them to centralized analysis engines, enabling continuous visibility and providing the raw data used for detection, investigation, and response.
- Centralized management console: All telemetry sent by endpoint agents flows into a centralized console, where it is normalized and correlated. Security teams use this console to configure policies, review alerts, and trigger response actions, allowing endpoint security controls to be enforced consistently from a single operational interface.
- Threat detection and behavioral analysis: Endpoint activity is analyzed using artificial intelligence and behavioral analysis engines to identify patterns associated with malware, ransomware, or unauthorized access. When deviations occur, the system flags abnormal behavior rather than relying solely on signatures, enabling accurate detection of malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access, including previously unknown threats.
- Automated incident response and containment: Once a threat is confirmed, predefined response workflows automatically execute. These workflows isolate affected endpoints, terminate malicious processes, and restrict network communication, stopping threat spread while reducing the need for manual intervention during critical incidents.
- Patch and vulnerability management: Ongoing endpoint maintenance focuses on identifying missing updates and known software weaknesses. Security patches and configuration updates are consistently applied to reduce exposure and maintain a secure, stable endpoint posture.
- Threat intelligence integration: Detection capabilities are strengthened by correlating endpoint activity with external threat intelligence indicators such as malicious IP addresses, file hashes, and attacker techniques. This added context supports faster identification of emerging and evolving threats.
- Human-led SOC monitoring and threat hunting: Security operations center analysts monitor alerts, validate detections, and investigate incidents. Human-led threat hunting identifies advanced or stealthy threats that automated systems may miss, ensuring deeper visibility and stronger endpoint protection.
What Are the Different Types of Endpoint Security Solutions?
Different types of endpoint security solutions include Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and Unified Endpoint Management (UEM). Each solution addresses a specific aspect of endpoint protection, detection, or management. In a managed endpoint security model, Managed Service Providers (MSPs) often combine these solutions to deliver layered defense, centralized visibility, and continuous response for organizations that lack in-house security resources.
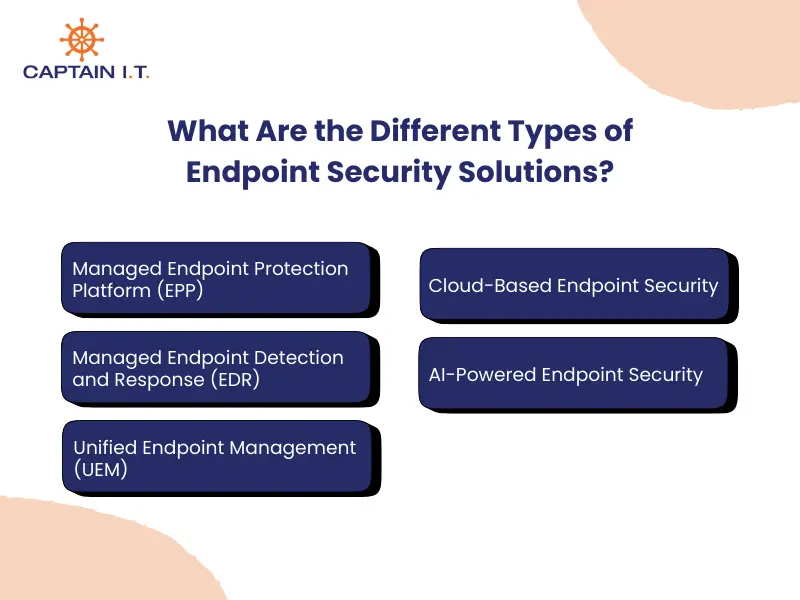
Managed Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP)
A Managed Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP) is a cloud-based security solution that provides foundational protection from common threats, including malware, ransomware, and zero-day attacks, using techniques such as behavioral analysis and threat intelligence. Through centralized management, real-time monitoring, and automatic updates, EPP enforces consistent security controls and helps maintain a stable and protected endpoint environment within a managed endpoint security framework.
- Antivirus and anti-malware protection: Detects and blocks known malware, ransomware, and malicious files through signature-based and heuristic scanning to prevent infections at endpoints.
- Firewall management: Enforces endpoint-level firewall rules to control inbound and outbound network traffic, reducing exposure to unauthorized connections and network-based attacks.
- Device and application control: Regulates which devices and applications can run on endpoints, limiting unauthorized software usage and reducing the overall attack surface.
Managed Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Managed Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a cybersecurity service that provides 24/7 monitoring, advanced threat detection, and expert-led response for endpoint devices. It goes beyond traditional antivirus by analyzing endpoint behavior to identify sophisticated and unknown threats in real time.
By combining advanced detection technology with human-led investigation and automated response actions such as endpoint isolation and process termination, managed EDR enables rapid containment of security incidents. This approach reduces attacker dwell time and strengthens the overall endpoint security posture without requiring dedicated in-house security expertise.
Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)
Offering a centralized management approach, Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) brings all end-user devices under a single control platform, regardless of operating system or location. This model enables organizations to manage, secure, and monitor PCs, smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices while applying consistent security policies and compliance controls across hybrid and remote work environments. By consolidating device administration with security enforcement, UEM streamlines IT operations, improves endpoint visibility, and ensures devices remain compliant and protected throughout their entire lifecycle.
Cloud-Based Endpoint Security
Cloud-based endpoint security protects endpoint devices such as laptops, servers, and mobile systems by using centralized, cloud-hosted platforms for real-time threat detection, prevention, and response. It offers scalable deployment, simplified management functions such as patching and monitoring, and advanced protection powered by AI and machine learning. This approach is well-suited for securing modern, distributed workforces and cloud-native infrastructure beyond the limits of traditional antivirus solutions.
AI-Powered Endpoint Security
Using machine learning and advanced analytics, AI-powered endpoint security identifies threats by analyzing patterns and deviations from normal endpoint behavior. This approach enables the detection of unknown, zero-day, and evolving attacks that traditional rule-based methods may miss. By continuously learning from endpoint telemetry and threat data, AI-driven security improves detection accuracy, reduces false positives, and supports faster, more adaptive responses within managed endpoint security environments.
What Are the Key Features of Managed Endpoint Security?
The key features of managed endpoint security include real-time monitoring, advanced threat detection, automated response actions, centralized management, and 24/7 SOC monitoring. When delivered by an MSP, this set of operational and security features works together to provide continuous protection, centralized visibility, and rapid response across endpoint devices, helping organizations maintain strong security outcomes without relying on in-house security teams.
7 key features of managed endpoint security:
- Real-time endpoint monitoring: Managed endpoint security continuously collects and analyzes endpoint telemetry such as process execution, file activity, and network connections. This enables immediate visibility into endpoint behavior and allows suspicious activity to be identified as soon as it occurs.
- Behavioral threat detection: Establishes a baseline of normal endpoint behavior and detects deviations that indicate malware, ransomware, or misuse. By focusing on behavior rather than signatures alone, it identifies unknown, zero-day, and fileless threats more effectively.
- Automated threat isolation and response: Triggers predefined response actions when a threat is detected, including isolating endpoints, terminating malicious processes, and blocking network communication. This automation limits lateral movement and reduces response time during active incidents.
- Centralized policy management: Enables security teams to define, deploy, and enforce endpoint security policies from a single console. Centralized control ensures consistent configuration, access controls, and enforcement across all devices, locations, and users.
- Continuous patch and vulnerability management: Scans endpoints for missing updates and known vulnerabilities and applies patches based on risk priority. This reduces exposure to exploitable weaknesses and maintains a secure endpoint baseline over time.
- Integrated threat intelligence feeds: Correlate endpoint activity with external threat intelligence, including malicious IPs, domains, file hashes, and attacker techniques. This contextual enrichment improves detection accuracy and accelerates the identification of emerging threats.
- 24/7 SOC monitoring and expert support: Provides around-the-clock monitoring by security analysts who validate alerts, investigate incidents, and guide remediation. Continuous SOC coverage ensures threats are addressed promptly, including during nights, weekends, and holidays.
What Are the Benefits of Managed Endpoint Security for Businesses?
Managed endpoint security offers proactive 24/7 support, threat detection, reduced overload, and scalability for both small and medium businesses (SMBs) and larger enterprises. These benefits help organizations of every scale to maintain strong security outcomes while reducing internal complexity and resource strain.
7 key benefits of managed endpoint security for businesses:
- Reduces security team workload:
Managed endpoint security reduces the workload on internal IT and security teams by shifting continuous monitoring, alert triage, and initial threat investigation to a managed service. Centralized platforms and expert validation filter out low-value alerts, preventing teams from being overwhelmed by noise. This allows internal staff to focus on strategic initiatives, system improvements, and business enablement rather than reactive, day-to-day security operations. - Provides 24/7 expert cybersecurity support
Cyber threats can occur at any time, which is why managed endpoint security delivers 24/7 expert cybersecurity support through a dedicated Security Operations Center (SOC) and experienced security teams. These experts provide continuous monitoring, investigation, and response by reviewing endpoint activity around the clock and acting on alerts immediately, regardless of time zone or business hours. This uninterrupted SOC-led coverage removes security gaps during nights, weekends, or staffing shortages and helps prevent incidents from escalating due to delayed intervention. - Enables real-time threat detection
Managed endpoint security enables real-time threat detection by continuously monitoring and analyzing endpoint activity as it occurs. Telemetry, such as process behavior, file changes, and network communication, is analyzed using behavioral analysis, threat intelligence, and machine learning to identify malicious activity in real time. Early detection through managed endpoint security reduces attacker dwell time, limits lateral movement, and prevents minor security events from escalating into data breaches, ransomware incidents, or extended system outages. - Lowers total cost of ownership
Cost efficiency is a key advantage of managed endpoint security, as it consolidates endpoint protection, detection, response, and monitoring into a single service. By relying on shared security platforms and expert oversight, organizations reduce the need for multiple tools, specialized personnel, and complex infrastructure. As a result, businesses gain enterprise-grade endpoint security with predictable operating costs, making advanced protection practical for both SMBs and larger enterprises. - Strengthens regulatory compliance
Managed endpoint security strengthens regulatory compliance like HIPAA, GDPR by ensuring consistent enforcement of security controls and continuous visibility across all endpoint devices. Centralized policy management, ongoing monitoring, and detailed security logging provide clear, auditable evidence of control effectiveness during assessments. As endpoint environments evolve, managed services continuously adjust policies and monitoring coverage, allowing organizations to maintain compliance without manual effort or operational disruption. - Scales with business growth
Scalability with business growth is a core advantage of managed endpoint security, as it allows organizations to expand their endpoint environments without increasing security complexity or risk. As new users, devices, and locations are added, protection scales automatically through standardized agents and centrally managed policies. This ensures consistent security coverage while avoiding the need for proportional increases in internal staff, tools, or operational overhead, enabling businesses to grow without introducing security gaps. - Accelerates incident response times
In the event of a breach, managed endpoint security accelerates incident response by enabling immediate containment and expert-led investigation to find the root causes as soon as a threat is detected. Automated workflows quickly isolate affected endpoints, terminate malicious processes, and restrict network access to stop further spread. Security analysts then investigate root causes and guide remediation, minimizing downtime, limiting business impact, and restoring normal operations more quickly.
What Security Risks Do Organizations Face Without Managed Endpoint Security?
Without managed endpoint security, organizations, especially SMBs, face elevated exposure to cyber threats, including malware, phishing, and unpatched software, due to limited visibility, delayed detection, and inconsistent response across endpoint devices. The absence of continuous monitoring, centralized control, and expert oversight increases the likelihood that threats go undetected and escalate into business-impacting incidents.
4 common security risks organizations face without managed endpoint security:
- Malware & Ransomware: In the absence of managed monitoring and response, malicious software can execute and spread across endpoints unchecked. Ransomware attacks may encrypt systems and disrupt operations, resulting in data loss, downtime, and financial losses.
- Insider Threats: Without continuous behavioral monitoring and activity analysis, malicious or negligent insider actions can go undetected. This leads to significant data breaches, intellectual property theft, or internal sabotage.
- Phishing & Social Engineering: Endpoint users remain vulnerable to deceptive emails and malicious links when endpoint activity is not continuously analyzed. Successful phishing attacks can result in credential theft, unauthorized access, and broader compromise of internal systems.
- Unpatched Software: Without centralized patch and vulnerability management, endpoints often run outdated software with known weaknesses. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access, escalate privileges, or deploy malware across the environment.
What Are the Top Managed Endpoint Security Tools and Software?
Top managed endpoint security tools and software include CrowdStrike Falcon, Trellix Endpoint Security, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, and Trend Micro Apex One, which are recognized for AI-driven, automated threat detection and response. These tools form the technical foundation of managed services, enabling continuous monitoring, centralized control, and rapid threat containment when combined with expert oversight.

Top 7 managed endpoint security tools and software are:
- CrowdStrike Falcon: Regarded for its AI-native, single-agent cloud platform that delivers high-performance breach prevention, advanced EDR, and 24/7 managed detection and response for modern endpoint environments.
- SentinelOne Singularity: Known for autonomous, AI-driven endpoint protection that enables real-time threat detection, mitigation, and response across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: A preferred choice for organizations using the Microsoft ecosystem, offering built-in threat detection, vulnerability management, and deep endpoint visibility integrated with Microsoft 365 security controls.
- Trellix Endpoint Security: Recognized for unified endpoint protection that combines threat prevention, behavioral detection, and policy enforcement within integrated security operations workflows.
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR: Designed to deliver extended detection and response by correlating endpoint, network, and cloud telemetry, improving investigation accuracy, and reducing incident response time.
- Carbon Black (VMware): Known for strong behavioral monitoring and endpoint visibility, enabling threat detection, incident investigation, and response within managed security environments.
- Trend Micro Apex One: Valued for its layered endpoint protection that combines machine learning, behavioral analysis, and automated response to defend against ransomware and emerging threats.
Managed Endpoint Security Best Practices and Strategies
Strategies such as implementing zero-trust access controls, enabling multi-factor authentication, and maintaining regular security patching are essential to maximizing the effectiveness of managed endpoint security. When applied consistently, these practices strengthen endpoint protection, reduce risk exposure, and support continuous visibility and rapid response across endpoint environments.
Best practices and strategies for managed endpoint security:
- Implement zero-trust access policies
Under a zero-trust model, the system assumes that no user or device is trustworthy by default, even those inside the network perimeter. Its role is to verify every access request based on identity, location, and device health. This practice ensures that even if an endpoint is compromised, the attacker cannot automatically access sensitive data or systems. - Enable multi-factor authentication across endpoints
MFA adds a vital layer of security by requiring multiple verification methods before granting access. By ensuring that a password alone is insufficient for login, MFA effectively neutralizes 99% of credential-based attacks, preventing hijacked endpoints from being used as gateways for unauthorized network access. - Maintain regular patch management schedules
Maintaining a strict update schedule ensures that known vulnerabilities are closed before they can be exploited. This proactive maintenance reduces the “attack surface” and allows the managed security system to focus on novel threats rather than preventable ones. - Conduct continuous security awareness training
Regular training equips employees to spot phishing, recognize suspicious activity, and report incidents. This turns your workforce into a human firewall, significantly reducing the likelihood of a successful initial breach. - Segment networks to limit threat spread
Network segmentation involves dividing a larger network into smaller, isolated sub-networks. Its role is to contain lateral movement. If a threat infects an endpoint in one segment, proper isolation prevents it from spreading to critical servers or financial databases in another, drastically reducing the blast radius of an attack. - Partner with trusted managed security providers
Managed security is only as effective as the expertise behind it, which means relying on a trusted service provider is important. Partnering with professional endpoint security providers ensures that your organization has access to elite SOC analysts and the latest threat intelligence 24/7. This partnership allows businesses, especially SMB’s, to offload the burden of monitoring while maintaining a superior security posture. - Regularly test and update security policies
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and yesterday’s security rules may not stop tomorrow’s attacks. By conducting regular red team exercises or penetration tests, organizations can identify gaps in their defences and update their security policies to reflect the current reality of cyber warfare.