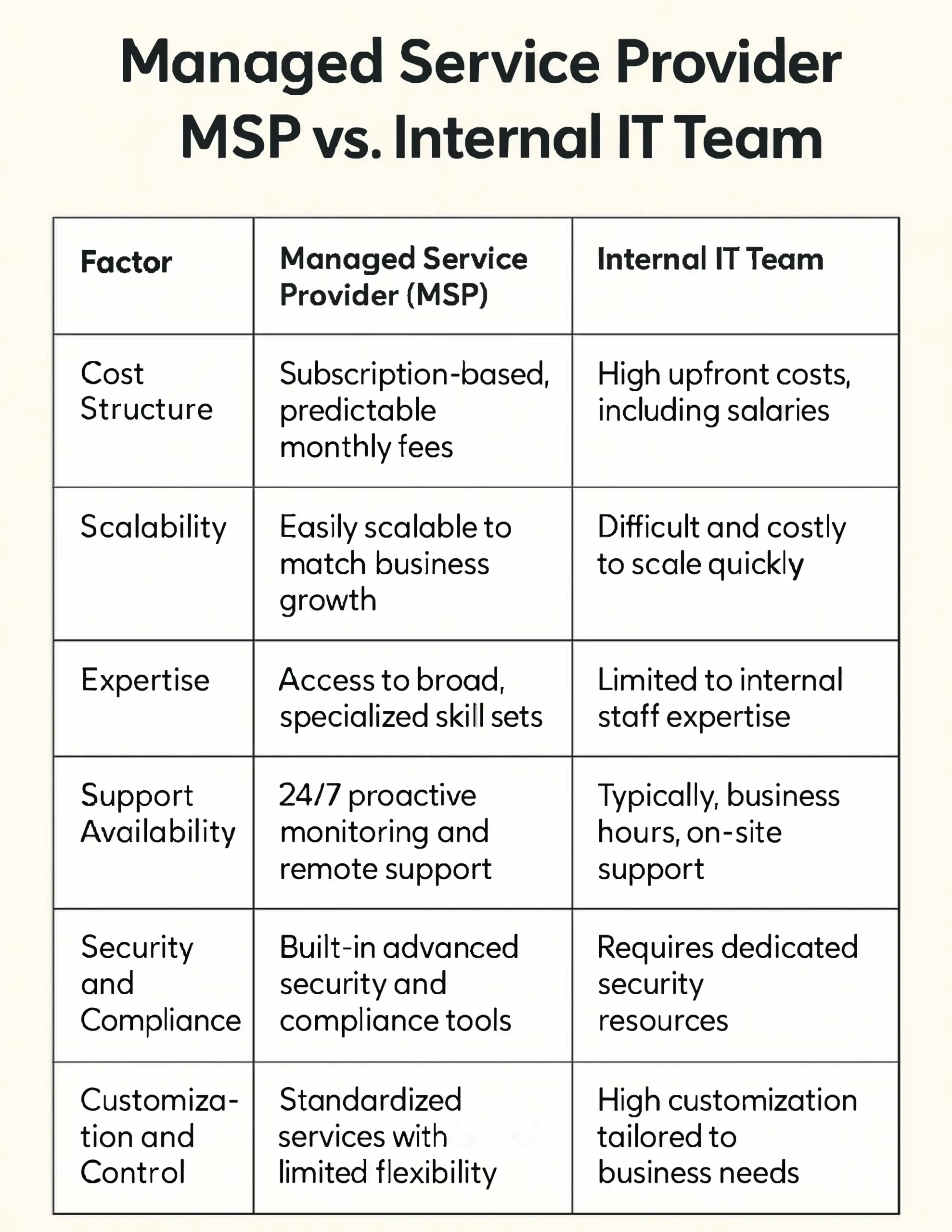
A Managed Service Provider (MSP) offers outsourced IT services with specialized expertise and proactive management, while an Internal IT Team consists of in-house employees who directly handle IT operations and support. Choosing between these two options can be challenging for business owners because each approach provides distinct advantages based on factors such as budget, IT complexity, and desired control over technology.
Internal IT Teams provide immediate, hands-on support and have strong knowledge of company systems, making them ideal for organizations needing close alignment between IT and business processes. In contrast, MSPs offer scalable services, advanced security, and broad expertise without the cost of full-time staff. The decision often depends on the company’s size, growth plans, and need for specialized skills.
Smaller businesses with complex IT needs often benefit from MSPs’ cost-effective management. Meanwhile, larger companies usually prefer Internal IT Teams for direct control and customization. Many organizations use hybrid models that combine both to balance flexibility and oversight. Understanding these options helps business owners make the best decision for their goals.
What is a Managed Service Provider?
A Managed Service Provider (MSP) is a third-party vendor that delivers continuous IT services and management to businesses. They assume responsibility for monitoring, maintaining, and supporting the IT infrastructure and applications remotely, ensuring system reliability, security, and operational efficiency.
Unlike traditional IT support, which reacts to problems as they occur, managed service providers take a proactive approach by preventing issues and optimizing technology performance. Traditional IT support generally responds to specific incidents, whereas managed service providers maintain ongoing management and strategic oversight to align IT with business objectives.
MSPs vary based on their service offerings and business focus. The 6 common types of MSPs include:
- Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs): Offer specialized cybersecurity, compliance, and risk management services that protect digital assets from threats.
- Cloud MSPs: Manage cloud infrastructure, oversee migration processes, and handle data storage to enable scalable computing environments.
- Network MSPs: Monitor and maintain network connectivity, ensuring consistent performance and uptime.
- Communication MSPs: Manage communication technologies such as email, messaging, video conferencing, and VoIP to enhance collaboration.
- Infrastructure MSPs: Handle hardware, software, and IT infrastructure management to maintain operational stability.
- Co-Managed IT MSPs: Collaborate with internal IT teams to augment IT capabilities and address complex challenges.
Pros of MSPs
Managed service providers offer organizations a structured and efficient way to manage their IT operations. Their services help businesses achieve greater stability and predictability in technology management while reducing risks associated with system failures and security threats. The primary advantages of MSPs include the following:
- Provide predictable IT costs through fixed monthly fees for easier budgeting.
- Improve system uptime by continuously monitoring and maintaining IT environments.
- Reduce security risks with timely updates and proactive threat detection.
- Offer access to specialized expertise and advanced technology without in-house investment.
- Enable internal IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives by handling routine tasks.
Cons of MSPs
While managed service providers bring many advantages, they also introduce certain challenges that organizations must consider. These drawbacks are listed below:
- Reduce direct control over certain technology decisions, potentially limiting flexibility.
- Incur fixed monthly costs that may be higher than occasional traditional IT support for smaller needs.
- Create dependency risks if the MSP experiences service disruptions or slow responses.
- May lack a deep understanding of unique organizational processes, leading to mismatched expectations.
- Require initial setup and integration, which can temporarily disrupt workflows.
What is an Internal IT Team?
An internal IT team is a group of employees within a company who manage and support its technology systems. This team handles tasks like fixing hardware, installing software, maintaining networks, and helping users with technical issues.
Unlike MSPs, the internal IT team works on-site and understands the company’s specific needs and culture. They keep control of all IT operations and make sure technology supports the company’s goals.
Pros of an Internal IT Team
Businesses that require complete control over IT management, business-specific IT solutions, and direct oversight benefit from an internal IT team. It is also advantageous for companies with high-security compliance needs, such as financial institutions and healthcare providers. Some of the key benefits of having an internal IT team are:
- Maintain direct control over technology decisions and operations.
- Provide immediate, hands-on support to reduce downtime.
- Develop deep knowledge of the company’s systems and culture.
- Align IT strategies closely with business goals.
- Foster strong communication with other departments.
Cons of an Internal IT Team
While an internal IT team offers customized IT infrastructure and management, it comes with cost, scalability, and expertise challenges that businesses must consider.
- Requires significant investment in hiring and training staff.
- May face limited resources during peak demand or complex projects.
- Need continuous learning to keep skills updated.
- Lack access to specialized expertise found in external providers.
- Can become isolated from the wider industry’s best practices.
How Can MSPs and Internal IT Teams Collaborate in a Hybrid Model?
MSPs and internal IT teams collaborate in a hybrid model by sharing responsibilities and combining their expertise to deliver comprehensive IT management that drives business growth. This collaboration enables businesses to scale technology operations efficiently, improve security posture, and reduce downtime.
By blending proactive MSP services with the internal team’s deep organizational knowledge, companies can accelerate innovation, optimize resource use, and respond swiftly to market changes. Understanding this partnership lays the foundation for exploring specific collaboration structures, such as the co-managed IT framework and consulting-based framework, which further define how these teams work together effectively.
Co-Managed IT Framework
The co-managed IT framework integrates managed service providers with internal IT teams to share responsibilities and resources. In this setup, MSPs handle routine maintenance, monitoring, and specialized tasks, while internal teams focus on strategic projects and business-specific requirements. This collaboration improves efficiency, reduces downtime, and enhances overall IT service quality. Co-managed IT frameworks enable organizations to extend their internal capabilities without the full cost of expanding in-house staff.
Here is how IT responsibilities are shared between an internal IT team and an MSP in a hybrid model.
| Internal IT Team | MSP |
| Manages proprietary software and industry compliance | Provides round-the-clock monitoring, cloud management, and proactive maintenance |
| Handles immediate support and device troubleshooting | Implements cybersecurity solutions, ensures compliance, and manages data backup |
| Oversees internal cybersecurity policies and employee IT training | Offers expertise in network optimization, threat intelligence, and disaster recovery |
Consulting-Based Framework
In the consulting-based framework, the managed service provider acts primarily as an advisor to the internal IT team. The MSP offers guidance, best practices, and strategic recommendations to help the internal team optimize technology management and align IT initiatives with business goals. This model empowers the internal team with expert knowledge, enabling better decision-making and improved IT outcomes. By serving as a consultant, the MSP supports continuous improvement and helps the organization adapt to evolving technology challenges.
How To Choose The Right MSP for Your Business?
To choose the right managed service provider (MSP) for your business, you should evaluate their industry expertise, service offerings, responsiveness, security measures, and scalability to ensure they align with your company’s specific needs and growth plans. Assessing these criteria helps guarantee that the MSP can deliver tailored, reliable IT support that drives efficiency and protects your technology environment.
Finding an MSP that meets these critical requirements can be challenging, but partnering with a provider like Captain IT brings proven experience and personalized service that eases the decision-making process. As a trusted MSP serving diverse industries across Southern California including Los Angeles, Riverside, Orange County, San Diego, and Irvine, Captain IT delivers customized solutions and dedicated support, helping businesses optimize their IT infrastructure and maintain seamless operations. This commitment makes Captain IT a dependable partner for long-term technology management.