Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting digital systems, data, and networks from cyber threats using specialized security types, including network, application, information, and cloud security. Each of these cybersecurity types targets specific vulnerabilities, working together to defend an organization’s digital infrastructure against risks like data theft, malware, and service disruptions.
With cybercrimes on the rise, the importance of robust and layered cybersecurity strategies cannot be overstated, especially among small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs). In 2024, the U.S. reported 859,532 cybercrimes, leading to financial losses totaling $16.6 billion (Source: USAFacts). This sharp rise in both the frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks underscores the critical importance of implementing strong protection measures.
To combat these growing threats, businesses rely on different types of cybersecurity, each playing a distinct role in defending systems, data, and networks. These cybersecurity types work in harmony to minimize vulnerabilities and strengthen defense mechanisms.
Here are the 9 types of cybersecurity that all work together to reduce cyber threats:
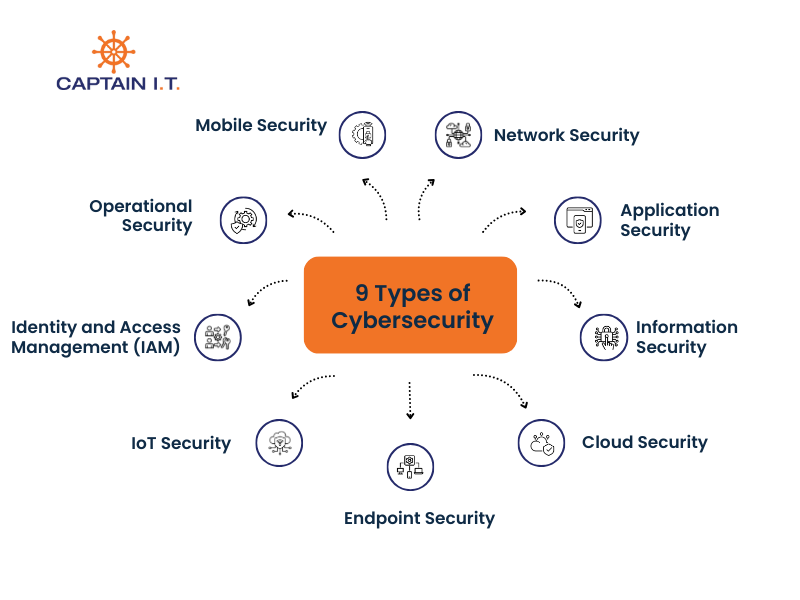
- Network Security: Protects network infrastructure using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, VPNs, and access controls.
- Application Security: Secures software applications with secure coding practices, patch management, code reviews, and input validation.
- Information Security: Ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data through encryption, access controls, and data backup protocols.
- Cloud Security: Secures cloud environments by managing identity access, encrypting cloud data, and preventing misconfigurations.
- Endpoint Security: Defends end-user devices such as laptops and mobile phones with anti-malware tools, phishing protection, and real-time monitoring.
- IoT Security: Secures internet-connected devices using firmware patching, device authentication, and communication controls.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Manages access control using multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and authorization checks.
- Operational Security: Establishes secure business processes, classifies sensitive data, and prepares for potential incidents.
- Mobile Security: Protects smartphones and tablets with mobile device management, jailbreak detection, and secure app controls.
Network Security
Network security is the practice of defending computer networks and data from unauthorized access, misuse, theft, or damage. It relies on a combination of hardware, software, policies, and processes to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad) of data. By protecting against threats like malware, ransomware, and phishing, network security aims to safeguard the entire network infrastructure, whether for large enterprises or small businesses. This involves controlling access to sensitive data, detecting potential threats, preventing attacks, and ensuring the stability of the network.
To effectively achieve these objectives, network security leverages a variety of tools and technologies, including firewalls, VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), antivirus and anti-malware software, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, and Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS). Together, these tools form a comprehensive network security framework that helps businesses, especially financial, healthcare, and retail, defend against security breaches and maintain the integrity of the network.
Application Security
Also known as AppSec, application security integrates security measures throughout the software development lifecycle to protect applications and their data from threats. It addresses vulnerabilities like SQL injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), weak authentication, and exposed APIs, ensuring that potential exploits are mitigated early. By embedding key strategies like secure coding, penetration testing, Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), and Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) into every stage of development, this cybersecurity approach reduces vulnerabilities before deployment.
Secure coding practices help developers avoid vulnerabilities, while Static and Dynamic Application Security Testing (SAST and DAST) identify flaws early in both the code and during runtime. Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) combines these methods for a more comprehensive assessment. Additionally, tools like Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) provide real-time protection during runtime, and Software Composition Analysis (SCA) ensures the security of third-party libraries.
Information Security
The practice of safeguarding information and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction is known as Information Security (InfoSec). InfoSec covers both digital and physical data, protecting everything from electronic records to physical documents of both individuals and businesses. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data (the CIA Triad) through a combination of tools and technologies like firewalls, encryption, and antivirus software.
In addition to these core measures, InfoSec employs cloud security and monitoring tools such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) to address risks such as data breaches and theft. Strong InfoSec policies are essential for maintaining business continuity, ensuring that systems remain operational even in the face of cyberattacks or other disruptions. These policies also help protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, safeguarding the privacy of customers, employees, and organizations. Moreover, InfoSec is vital for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA, making it crucial for businesses of all sizes, from large enterprises to small organizations.
Cloud Security
Cloud security refers to the policies, practices, controls, and technologies used to safeguard applications, data, and infrastructure in cloud environments. IBM reports that 80% of breaches involving sensitive data stored in the cloud (public, private, or hybrid), highlighting the importance of strong cloud security. Its primary focus is ensuring secure storage, network protection, access management, and disaster recovery while defending against internal and external threats. Key cloud security components include data encryption, Identity and Access Management (IAM), firewalls, and endpoint security.
Additionally, cloud security also ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud resources, while preventing unauthorized access and other cyber threats. A robust cloud security strategy follows a shared responsibility model where cloud providers are responsible for securing the cloud infrastructure, while clients are responsible for securing their data and applications. This collaborative approach strengthens security, particularly in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and technology.
Endpoint Security
The cybersecurity practice of protecting devices (endpoints) like desktops, laptops, and mobile devices that connect to a network against cyber threats like malware and phishing is known as endpoint security. This protection process is done using software and strategies to monitor, detect, and block malicious activity at the entry point of the network. Its key components include data loss prevention (DLP) to prevent unauthorized data transfers, behavioral analysis to identify unusual activity, endpoint detection and response (EDR) to provide real-time monitoring and remediation, and firewalls with network control to block malicious traffic.
Together, these elements work to safeguard both data and networks from cyber threats. Additionally, endpoint security protects both physical and virtual servers, IoT devices like sensors and digital signage, and even point-of-sale (POS) systems. It is especially critical in remote work environments and mobile workforces, where devices are more exposed to external threats. A comprehensive endpoint security strategy ensures that devices across various endpoints are secured, safeguarding data and networks from cyber threats.
IoT Security
IoT security is a branch of cybersecurity dedicated to protecting Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the networks they connect to from cyber threats such as unauthorized access and data breaches. Many IoT devices have inherent vulnerabilities due to their design, which prioritizes functionality over security, making them susceptible to exploitation. Since these devices collect and transmit sensitive data, preventing data breaches is crucial to safeguarding that information from theft or unauthorized access.
Additionally, maintaining system integrity is vital, as compromised IoT devices can serve as gateways for attacks on other systems within a network, potentially causing widespread damage. For maximum security, IoT security strategies should include regular firmware updates, secure communication protocols, strong device authentication, and robust risk management practices to address vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation. Therefore, a comprehensive IoT security strategy is essential to effectively mitigate risks for both the devices and the networks they connect to.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Another important cybersecurity measure is Identity and Access Management (IAM), a framework that ensures the right individuals have access to the appropriate resources at the right time. IAM encompasses policies, processes, and technologies designed to control access to systems, applications, and data, ensuring that information remains confidential, intact, and available. It primarily functions through two core processes, authentication, which verifies a user’s identity, and authorization, which determines the actions a user is permitted to take. Role-based access control (RBAC) is often used to assign roles and permissions based on job responsibilities.
A major benefit of IAM is its ability to enhance security by ensuring that only authorized individuals can access or perform actions on sensitive systems. This is achieved by verifying identities and managing permissions in a structured manner, ensuring that each user has access only to the resources necessary for their role. Additional IAM components, such as Single Sign-On (SSO), improve both security and user convenience by allowing access to multiple applications with a single login.
Operational Security
Operational security (OPSEC) is a strategic process designed to protect sensitive information by identifying key data, assessing potential threats and vulnerabilities, and implementing countermeasures from the perspective of potential adversaries. Its primary objective is to prevent unauthorized access to information that could jeopardize operations, whether through physical security breaches, cybersecurity threats, or other methods. This makes it perfect for anyone handling sensitive information, especially in the military, government, and business.
OPSEC is crucial in preventing data leaks by ensuring that even seemingly harmless actions do not inadvertently expose sensitive information. It protects vital data, maintains operational integrity, and preserves a competitive advantage. To achieve this, OPSEC includes key components such as data classification, risk assessment, incident response, and security protocols. Furthermore, OPSEC enhances cybersecurity by working together with other cybersecurity strategies to form a more comprehensive and resilient security framework.
Mobile Security
Mobile security is a critical cybersecurity practice that focuses on protecting smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices from cyber threats such as malware, unauthorized access, and data leakage. With mobile devices being widely used and often connected to public networks, securing mobile endpoints has become increasingly important for both personal and organizational data protection. As mobile devices continue to play a central role in daily life and business operations, the need for robust security measures has never been greater.
This is especially true in environments like BYOD (Bring Your Own Device), where employees use their personal devices for work. Mobile security relies on key features such as app control, data encryption, jailbreak detection, and defenses against malicious apps to establish a strong protection framework. These measures work together to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data, ensuring both employee privacy and corporate security are maintained.
How does cybersecurity protect small businesses from attacks?
Cybersecurity protects small businesses by establishing a multi-layered defense system that integrates people, processes, and technology to prevent, detect, and recover from digital threats. Since SMBs typically have weaker defenses compared to larger corporations, they are often prime targets for cybercriminals. Robust cybersecurity is essential for protecting sensitive customer data, financial records, and ensuring business continuity.
Additionally, the need for strong cybersecurity for small businesses is emphasized by recent statistics, with 61% of small businesses reporting at least one cyberattack in the past year. Among the different types of cyber threat malware is the most common, affecting 18% of businesses, followed by phishing attacks, which target 17%. Data breaches also concern 16% of small businesses, while website hacks affect 15%, highlighting the critical importance of securing online assets. (Source: SQ Magazine).Given these risks, implementing effective cybersecurity measures is not just a luxury for small businesses but a necessity. By investing in cybersecurity through reliable cybersecurity service providers, small businesses can prevent cyber attacks, maintain customer trust, avoid financial losses, and ensure sustainable, secure growth.