When small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) face frequent downtime, rising cybersecurity risks, or unpredictable IT expenses, their internal IT teams often struggle to keep up. Limited staff cannot provide constant monitoring or rapid response, which leaves gaps in security and efficiency. To address these challenges, many organizations turn to managed IT services, which provide a structured way to outsource key technology operations to ensure stability, protection, and cost control.
Through managed IT services, businesses gain access to essential functions such as infrastructure monitoring, help desk support, cybersecurity management, cloud oversight, compliance preparation, and disaster recovery planning. These services are designed to reduce downtime, safeguard data, and maintain continuity during disruptions. Delivery is typically handled by a Managed Service Provider (MSP), which operates under service level agreements (SLAs) that define accountability and performance standards.
The real value of managed IT services lies in balancing reliable performance with cost efficiency. To achieve this, businesses must weigh risks such as vendor dependency or SLA misalignment while considering costs shaped by service scope, user or device counts, and security needs.
What Are Managed IT Services?
Managed IT services are outsourced IT tasks where a third-party vendor (MSP) manages daily technology operations for a business. They help improve reliability, reduce costs, and give organizations access to enterprise-level expertise without maintaining a full in-house team.
Core components of managed IT services include remote monitoring to detect issues before downtime, help desk support for user assistance, cybersecurity management with firewalls and threat detection, and cloud solutions that ensure scalability and flexibility. These services are typically delivered under a service level agreement (SLA), which sets clear performance standards and accountability, giving businesses both reliability and cost predictability.
What are the Core Functions of Managed IT Services?
The core functions of managed IT services cover monitoring, support, security, and system management that keep business technology reliable and cost-efficient. These functions typically include infrastructure oversight, user support, cloud and network management, cybersecurity, compliance, and performance reporting, each designed to reduce downtime and strengthen continuity.
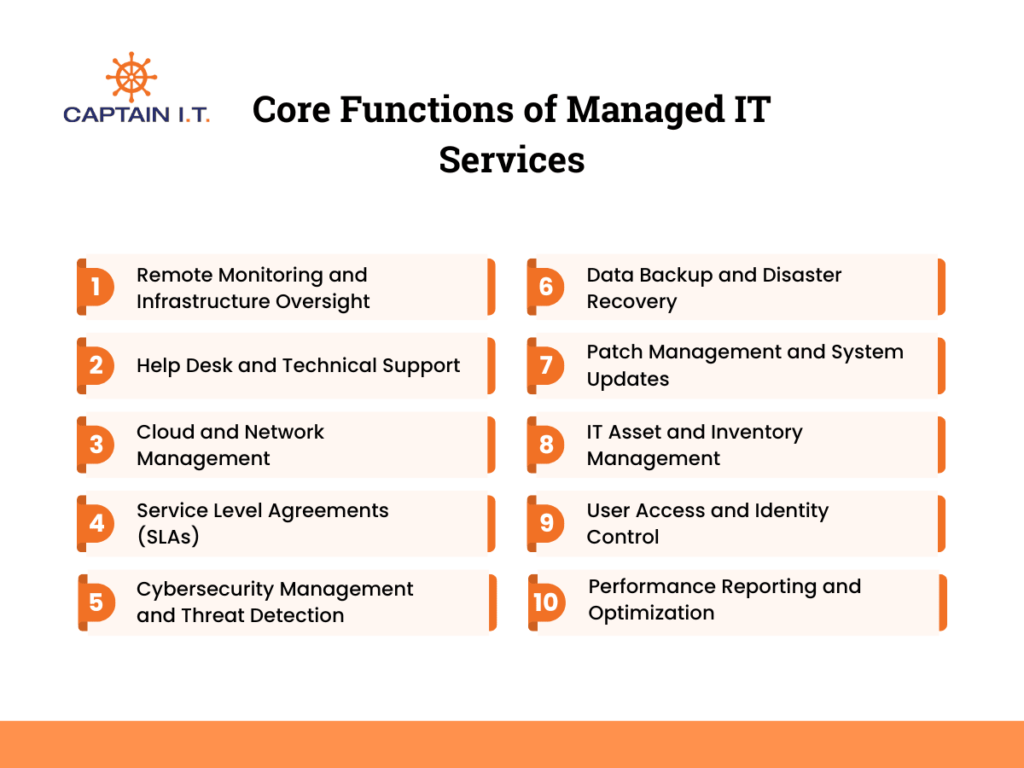
Remote Monitoring and Infrastructure Oversight
Remote monitoring in managed IT services means having IT infrastructure supervised in real time by a Managed Service Provider (MSP). It involves continuous oversight of servers, networks, and devices to ensure systems remain healthy and responsive at all times.
Typical capabilities include 24/7 uptime tracking, diagnostics of hardware and networks, and instant alerts for unusual activity. By detecting issues early, businesses experience fewer outages, faster problem resolution, and lower operating costs, which keeps operations reliable and efficient.
Help Desk and Technical Support
The help desk is the frontline IT support service in managed IT, offered by Managed Service Providers (MSPs) to resolve user issues quickly and consistently. It serves as the first point of contact for employees needing technical assistance, ensuring that problems are addressed without overwhelming internal IT teams.
Support typically includes Tier 1 help for common issues, Tier 2 and Tier 3 for advanced troubleshooting, ticketing systems to track progress, and escalation protocols for complex cases. Help desk support services are governed by service level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee response times. The result is minimized user downtime, a consistent IT experience across the organization, and documented service performance for accountability.
Cloud and Network Management
Reliable connectivity and secure cloud operations are essential for business performance, and managed IT services ensure both by having providers manage cloud environments and physical network infrastructure. This approach gives organizations confidence that their systems are continuously supported and aligned with business needs.
Key responsibilities include provisioning new resources, monitoring performance, configuring firewalls and routing, and optimizing connectivity across locations. By outsourcing these functions to an MSP, companies gain dependable reliability, stronger protection against network risks, and scalable solutions that adapt to both hybrid and cloud-native environments.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Businesses rely on service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure managed IT services are delivered consistently and meet agreed standards. An SLA is a formal contract that defines the scope, quality, and responsibilities between the organization and the Managed Service Provider.
Typical elements include guaranteed response times, resolution targets, uptime commitments, and penalties for non-compliance. By setting clear metrics, SLAs create accountability and transparency, helping businesses trust that their IT operations will remain stable while providers are held responsible for performance.
Cybersecurity Management and Threat Detection
Managed IT services strengthen business resilience by providing continuous cybersecurity management and proactive threat detection. This ensures that sensitive data, networks, and applications remain protected against both common risks and advanced cyberattacks.
Core services include firewall configuration, endpoint protection, antivirus updates, and continuous threat detection with real-time monitoring. By applying these measures, businesses reduce the likelihood of breaches, maintain compliance with standards such as HIPAA or GDPR, and gain confidence knowing their IT environment is continuously protected.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Unexpected outages or cyber incidents can halt business operations, which is why managed IT services include data backup and disaster recovery to keep systems protected. These services ensure that critical information is preserved and quickly restored when disruptions occur.
Common practices include scheduled backups, off-site or cloud replication, encryption, and disaster recovery testing. By defining recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), businesses gain confidence that they can resume operations with minimal downtime and data loss. This proactive approach protects productivity, revenue, and customer trust.
Patch Management and System Updates
Patch management in managed IT services refers to keeping software and systems up to date to close security gaps and improve performance. It ensures that known vulnerabilities are addressed before attackers can exploit them.
Providers handle tasks such as scheduled patch rollouts, urgent security updates, and compliance-driven patching for standards like PCI-DSS. With consistent updates, businesses reduce exposure to cyber threats, improve system stability, and meet regulatory requirements, all while minimizing downtime.
IT Asset and Inventory Management
As part of managed IT services, asset and inventory management gives businesses control over hardware, software, and licenses to ensure efficient use and compliance. MSPs maintain visibility into resources across their lifecycle, helping organizations stay organized and cost-effective.
Typical responsibilities include inventory tracking, license compliance checks, warranty monitoring, and planning for hardware or software refresh cycles. By managing assets proactively, businesses improve budgeting, avoid unnecessary purchases, and remain ready for audits or regulatory reviews.
User Access and Identity Control
In managed IT services, user access and identity control protect business systems by regulating who can access IT resources and when. This function ensures sensitive data and applications remain secure and available only to authorized users.
Managed Service Providers enforce identity protocols through role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regular access audits to detect outdated or risky permissions. These measures improve overall security, reduce insider threats, and help businesses remain compliant with industry regulations such as HIPAA or GDPR.
Performance Reporting and Optimization
Performance reporting in managed IT services provides businesses with clear visibility into how their systems are operating. It serves as a feedback loop that tracks key IT activities and identifies areas that need improvement.
Reports often include metrics such as system uptime, incident frequency, ticket resolution times, and infrastructure usage analysis. By reviewing these insights, businesses can make data-driven decisions, optimize IT performance, and ensure accountability from their Managed Service Provider (MSP). This transparency leads to proactive improvements and stronger long-term reliability.
Why Are Managed IT Services Important?
Managed IT services are important to help businesses maintain continuity, reduce downtime, improve security, and control costs through predictable service models. By outsourcing essential IT functions to an MSP, companies gain access to expert support, compliance readiness, and scalable solutions that allow internal teams to focus on growth and innovation.

Business Continuity Enablement
By keeping critical systems available during disruptions, managed IT services help businesses stay resilient in times of crisis. MSPs secure operations with automated backups and disaster recovery planning, reducing the risk of costly interruptions when unexpected events occur. They also provide proactive monitoring to detect issues early and resolve them before they escalate. With these safeguards in place, businesses minimize downtime, maintain productivity and revenue, and preserve customer trust even under challenging conditions.
Operational Downtime Reduction
Managed IT services reduce operational downtime by combining 24/7 system monitoring, automated alerts, and proactive maintenance to detect and fix issues before they interrupt workflows. Providers handle software patching, hardware diagnostics, and network performance checks while also applying root cause analysis to prevent recurring problems. With clear escalation paths and rapid response protocols, businesses avoid costly outages, sustain employee productivity, and deliver uninterrupted service to customers.
IT Burden Reduction for Internal Teams
Overloaded IT teams often struggle to balance daily support with long-term projects, and managed IT services solve this by taking on routine tasks. Providers manage responsibilities such as monitoring, patching, and user support, giving in-house staff the time and capacity to focus on innovation and strategic initiatives. This shift enhances efficiency, prevents staff burnout, and ensures that internal expertise is leveraged to advance business priorities rather than being consumed by maintenance.
Cost Control and Predictability
By standardizing IT expenses into clear pricing models, managed IT services help businesses achieve cost control and financial predictability. Providers typically offer flat-fee, per-user, or per-device plans, covering essentials like monitoring, help desk support, and cybersecurity under one contract. This approach not only simplifies budgeting but also ensures that unexpected issues, such as system failures or security incidents, are resolved without additional costs. With predictable spending, organizations can plan long-term investments confidently and scale IT resources as their needs evolve.
Enhanced Security Posture
Strong cybersecurity is essential for protecting business operations, and managed IT services deliver this by embedding advanced security measures into daily IT management. Providers use firewall management, endpoint protection, antivirus updates, and continuous threat detection to safeguard against evolving threats. This proactive approach lowers the risk of breaches, helps meet compliance standards such as HIPAA or GDPR, and gives organizations peace of mind knowing their systems and data are continuously protected.
Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Through managed IT services, businesses can meet regulatory requirements while reducing exposure to compliance gaps and legal risks. Providers support this by maintaining audit logs, enforcing access controls, conducting risk assessments, and preparing documentation for audits. They also align systems with frameworks such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or GDPR to ensure ongoing compliance. With these measures in place, organizations lower the chance of fines or penalties, strengthen accountability, and protect their reputation by keeping operations both secure and regulation-ready.
Strategic Resource Reallocation
Managed IT services enable businesses to reallocate internal resources from routine IT maintenance to strategic projects that drive growth. By outsourcing tasks such as monitoring, patching, and help desk support, in-house teams gain the capacity to focus on initiatives like cloud migration, digital transformation, and technology innovation. This approach improves agility, accelerates business outcomes, and boosts staff morale by ensuring IT expertise is applied to advancing goals instead of day-to-day troubleshooting.
What are the Benefits of Managed IT Services for Business?
Managed IT services deliver measurable benefits, including reduced downtime, stronger cybersecurity, predictable costs, and scalable IT resources. By outsourcing routine functions to a provider, organizations gain real-time system visibility, faster issue resolution, and support for compliance, while freeing internal teams to focus on innovation. This combination improves efficiency, protects revenue, and ensures long-term business continuity, highlighting the benefits of managed IT services for sustainable growth.
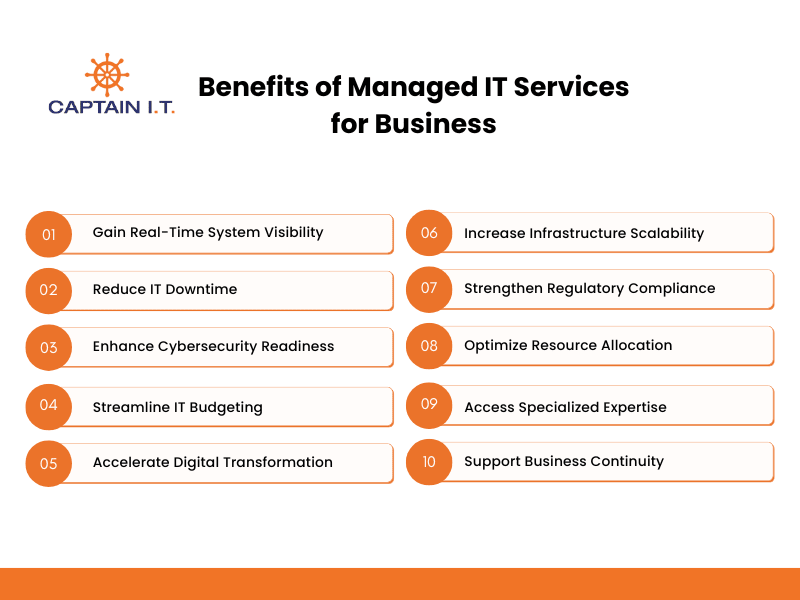
Gain Real-Time System Visibility
Real-time visibility into IT systems is made possible through managed IT services that provide monitoring dashboards, automated alerts, and performance diagnostics. This visibility not only allows businesses to track uptime, detect issues instantly, and analyze resource usage but also supports long-term planning by identifying trends and performance bottlenecks. With actionable insights into system health, organizations can resolve problems proactively, optimize infrastructure, and maintain reliable operations with greater confidence.
Reduce IT Downtime
System downtime can disrupt operations, cause revenue loss, and damage customer trust, but managed IT services minimize these risks through 24/7 monitoring, automated alerts, and proactive maintenance that detect and resolve issues before they escalate. Providers also apply patches quickly and use rapid response protocols to keep systems stable. With fewer disruptions, businesses maintain productivity, meet SLA targets, and deliver reliable services to customers.
Enhance Cybersecurity Readiness
With cyber threats growing more frequent and complex, managed IT services enhance security readiness by providing continuous monitoring and defense. Providers deliver layered protection through firewalls, endpoint security, vulnerability scanning, and real-time threat detection. They also implement incident response protocols to contain attacks quickly and minimize damage. This proactive approach reduces the risk of breaches, supports compliance with regulations, and builds customer trust by keeping business data and systems secure.
Streamline IT Budgeting
Managed IT services streamline budgeting by replacing unpredictable expenses with clear, predictable pricing models. MSPs typically offer flat-fee, per-user, or per-device plans that cover essentials like monitoring, support, and security under one agreement. This structure gives businesses financial clarity, stabilizes cash flow, and allows leaders to plan long-term technology investments with greater confidence. By eliminating surprise costs, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and ensure IT spending aligns with strategic goals.
Accelerate Digital Transformation
Digital transformation drives growth and competitiveness, and managed IT services help businesses achieve it by enabling faster adoption of modern technologies. Providers guide initiatives such as cloud migration, SaaS deployment, automation, and hybrid cloud integration while ensuring day-to-day operations remain stable. With expert planning and support, organizations shorten project timelines, minimize disruption, and introduce new workflows with confidence. This allows businesses to innovate faster, improve efficiency, and stay ahead in a digital-first marketplace.
Increase Infrastructure Scalability
By adapting IT resources to business growth, managed IT services make it easier for organizations to scale without disruption. Providers deliver cloud provisioning, modular platforms, and on-demand resources that expand capacity as needs change, whether for new users, remote offices, or hybrid environments. This flexibility prevents costly reinvestments, ensures systems grow alongside the business, and helps companies pursue expansion with confidence while maintaining efficiency and reliable performance.
Strengthen Regulatory Compliance
Through managed IT services, businesses can strengthen regulatory compliance and avoid costly penalties or reputational harm. Providers enforce security policies, maintain audit logs, implement data governance controls, and prepare documentation required for standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS. These practices reduce legal risk, improve audit readiness, and build customer and partner trust by showing that sensitive data is managed securely and in line with regulations.
Optimize Resource Allocation
Managed IT services help businesses get more value from their people and budgets by optimizing how resources are used. Providers take over routine IT functions such as monitoring, patching, and help desk support, which reduces the time and costs tied to daily maintenance. This allows in-house teams to focus on strategic initiatives like digital transformation or cloud adoption. The result is higher workforce productivity, improved cost efficiency, and stronger returns on IT investments.
Access Specialized Expertise
Access to specialized expertise via managed IT services gives businesses an advantage in addressing complex IT challenges that internal teams may not be equipped to handle. Providers bring certified professionals skilled in areas such as cybersecurity, cloud infrastructure, and compliance, ensuring organizations receive enterprise-level support. This expertise allows problems to be solved faster, technology decisions to be better informed, and IT strategies to align with industry best practices.
Support Business Continuity
By protecting systems against outages and disruptions, managed IT services help businesses remain resilient and protect both revenue and customer confidence. MSPs deliver safeguards such as regular data backups, disaster recovery strategies, and infrastructure redundancy to ensure critical operations can recover quickly. With these measures in place, organizations minimize downtime, maintain consistent service delivery, and preserve both revenue and customer trust during unexpected events.
Challenges and Limitations of Managed IT Services
The main challenges of managed IT services include vendor lock-in, limited customization, SLA misalignment, and reduced control over IT systems. Businesses may also encounter unclear accountability for security and compliance, which can create risks if not addressed. By recognizing these limitations early and defining clear agreements, organizations can minimize potential drawbacks while still benefiting from reliable, cost-efficient IT support.
Risk of Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in occurs when businesses become dependent on a single managed IT provider, making it difficult or costly to switch. This risk often arises from proprietary tools, complex data migrations, or restrictive contracts that limit flexibility. Over time, lock-in can reduce negotiating power and hinder adaptability. To avoid this, organizations should prioritize providers that use open standards, negotiate clear exit terms, and ensure data portability from the outset.
Limited Customization or Flexibility
When managed IT services lack customization, businesses may struggle to align provider solutions with their specific needs. Standardized service models and rigid toolsets can create gaps for organizations with specialized workflows or custom applications. This limitation reduces flexibility and may slow down innovation. To overcome it, companies can negotiate tailored options upfront or choose co-managed IT models that blend provider support with internal expertise.
Service Level Agreement (SLA) Misalignment
Clear service level agreements are essential for reliable IT support, but misalignment can occur when contract terms do not match business priorities. Problems often stem from vague performance metrics, undefined response times, or missing penalties for non-compliance. These gaps reduce accountability and leave critical needs unmet. To avoid this, companies should negotiate SLAs with measurable metrics, enforceable response targets, and terms that reflect operational goals.
Loss of Direct Control Over IT Systems
Outsourcing IT to a managed service provider can limit a business’s direct control over its systems. Common issues include restricted administrative access, delays in making changes, and reliance on ticket-based processes for even minor tasks. This reduced visibility can slow decision-making and create frustration for internal teams. To address these challenges, businesses should establish clear escalation paths or adopt co-managed IT models that balance provider support with internal oversight.
Security and Compliance Accountability Gaps
Shared responsibility between businesses and managed service providers can create gaps in security and compliance. Unclear ownership of tasks like patching, encryption, or log retention may lead to oversights that increase regulatory and legal risks. These accountability gaps can leave organizations vulnerable during audits or incidents. To prevent them, companies should establish responsibility matrices, document policies, and conduct regular compliance audits to ensure clear alignment between provider and internal teams.
How Much Does Managed IT Services Cost?
The cost of managed IT services typically ranges from $50–$150 per user or $75–$250 per device per month, with advanced needs sometimes exceeding $500 per user or device. Actual costs depend on factors such as service scope, number of users or devices, and compliance or cybersecurity requirements. By matching services to business priorities and carefully reviewing contracts, organizations can estimate expenses more accurately and avoid unexpected fees, helping businesses understand managed IT services cost more effectively.
Managed IT Pricing Models
Flexible pricing options allow businesses to choose a managed IT service structure that fits their budget and support needs. Providers typically offer several managed IT pricing models, each with its own advantages:
- Per-user pricing: A set fee for each employee supported, typically ranging from $50–$150 per user per month.
- Per-device pricing: Charges based on the number of desktops, servers, or mobile devices, usually around $75–$250 per device per month.
- Flat-rate plans: One monthly fee that bundles multiple services, often $1,500–$8,000+ per month, depending on company size and coverage.
- Tiered pricing: Different service levels at varying price points, for example, basic ($50/month), standard ($100/month), and premium ($150+/month).
- Usage-based pricing: Pay only for the resources or services consumed, commonly starting at $200–$500 per instance or service usage.
These models allow organizations to align IT spending with service requirements, ensuring cost control without sacrificing support.
What Influences Pricing?
The cost of managed IT services is influenced by several factors that determine the level of support and protection a business receives. Key drivers include:
- Number of users or devices: More endpoints increase monthly fees.
- Service level agreements (SLAs): Higher availability and faster response times cost more.
- Cybersecurity requirements: Advanced protections raise pricing tiers.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Offsite storage and recovery planning add to costs.
- Compliance scope: Regulations like HIPAA, SOC-2, or PCI-DSS require additional controls.
By defining these needs clearly, organizations can obtain accurate quotes and avoid unexpected expenses.
How to Estimate Costs Accurately?
The best way to estimate managed IT service costs accurately is to plan systematically and match business needs with provider pricing models. Businesses should follow these steps:
- Identify the number of users and devices to be supported.
- Define required services, such as 24/7 support or cybersecurity coverage.
- Match needs to pricing model (per-user, per-device, or flat-rate).
- Request quotes from multiple providers to compare options.
- Review contracts for hidden fees and evaluate the total cost of ownership.
Types of Managed IT Services
Managed IT services range from core infrastructure support, such as network management and cloud solutions, to specialized functions like cybersecurity, backup and recovery, help desk support, and compliance advisory. These types of managed IT services cover both technology operations and end-user support, giving businesses the flexibility to select or combine services. This ensures that organizations can align their technology support with their specific needs and long-term goals.

Network and Infrastructure Management
As the backbone of managed IT services, network and infrastructure management covers all connected systems that support daily business operations. Providers configure routers and switches, manage bandwidth, ensure secure connectivity, and optimize traffic flow across offices and remote locations. They also monitor network health, perform diagnostics, and apply performance tuning to maintain stability. With proactive infrastructure management, businesses reduce latency, prevent outages, and maintain scalable networks that can adapt to growth and evolving demands.
Cloud Solutions and Data Services
Modern businesses depend on the cloud for agility and efficiency, and managed IT services provide the expertise to manage these environments effectively. Through MSPs, they deliver server hosting, SaaS deployment, secure data storage, and cross-platform migrations to keep systems connected and reliable. They also integrate cloud platforms with existing infrastructure to improve collaboration and performance while ensuring security and compliance. With managed cloud support, organizations gain scalability, flexibility, and reduced reliance on expensive on-premise hardware, enabling smoother digital transformation.
Cybersecurity Services
With cyberattacks becoming more frequent and sophisticated, cybersecurity services within managed IT provide the protection businesses need to stay secure. Using real-time monitoring, firewall management, endpoint protection, antivirus updates, and vulnerability scans, external service providers safeguard systems from threats. They also implement incident response protocols to contain and remediate attacks quickly, while applying threat intelligence to prevent repeat incidents. These measures reduce the risk of breaches, ensure regulatory compliance, and strengthen customer trust by demonstrating that sensitive data is continuously protected.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Protecting data and ensuring fast recovery after disruptions are core functions of managed IT services delivered through backup and disaster recovery. Providers schedule regular backups, replicate data to cloud or offsite locations, encrypt sensitive files, and perform recovery testing to confirm reliability. They also help businesses define recovery point objectives (RPOs) and recovery time objectives (RTOs) to set clear expectations. With these safeguards in place, organizations minimize downtime, maintain business continuity, and restore critical systems after cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters.
Help Desk and End-User Support
A key function of managed IT services is providing help desk and end-user support to resolve technical issues quickly and keep staff productive. Managed Service Providers deliver tiered assistance, from Tier 1 help with simple requests like password resets to Tier 2/3 for advanced troubleshooting. Using ticketing systems and SLA-driven escalation protocols, issues are tracked 24/7 and resolved efficiently. This structured approach minimizes downtime, ensures a reliable user experience, and improves overall employee satisfaction.
Patch Management and System Updates
Keeping software and systems up to date is essential for security, which is why managed IT services include patch management and system updates as a core function. Providers schedule routine patch rollouts, apply urgent hotfixes for vulnerabilities, and handle compliance-driven updates such as PCI-DSS requirements. They also manage updates across third-party applications and operating systems to close gaps often exploited by attackers. This proactive approach reduces the risk of breaches, minimizes downtime, and ensures systems remain stable, compliant, and optimized for performance.
Managed Communications and VoIP
As part of managed IT services, managed communications and VoIP provide businesses with reliable, modern communication tools that support remote and hybrid work. MSPs handle VoIP setup, call routing, video conferencing integration, and unified communications platforms (UCaaS) to streamline connectivity. Advanced features like call analytics, mobile integration, and cloud-based phone systems make collaboration easier across teams. These solutions reduce telecom costs, scale easily as businesses grow, and enhance productivity by giving employees flexible communication systems that work seamlessly across devices and locations.
IT Asset and Inventory Management
Within managed IT services, IT asset and inventory management ensures businesses maintain visibility and control over their technology resources. Providers track hardware and software through asset tagging, license monitoring, warranty checks, and lifecycle reporting. They also use automated tools to generate alerts for upcoming renewals or expiring warranties. This proactive oversight helps organizations reduce waste, avoid compliance risks from expired licenses, and plan upgrades more effectively. By keeping assets organized and costs predictable, businesses maximize the value of their IT investments.
Compliance and Risk Advisory Services
Staying compliant with regulations is critical for avoiding penalties, and managed IT providers deliver this support through compliance and risk advisory services. They perform risk assessments, conduct gap analyses, implement security and governance controls, and prepare documentation for audits across frameworks like HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC 2. MSPs may also conduct employee training and policy reviews to strengthen overall governance. These services reduce legal exposure, strengthen accountability, and give leaders confidence that IT operations consistently meet regulatory standards and industry expectations.
Remote Monitoring and Performance Reporting
A core function of managed IT is remote monitoring and performance reporting, which ensures businesses maintain visibility, reliability, and accountability across their IT systems. Providers deliver real-time alerts, performance dashboards, SLA tracking, and historical trend analysis to keep infrastructure secure and stable. Detailed reports also highlight usage patterns, recurring issues, and opportunities for optimization. With these insights, businesses can resolve problems before they escalate, minimize downtime, and make proactive decisions backed by transparent evidence of service quality.
How Managed IT Services Help With Security & Compliance?
Managed IT services help businesses stay secure and compliant by combining proactive cybersecurity measures with regulatory support. Providers monitor systems in real time, manage firewalls, apply patches, and protect data through encryption and backups, while also aligning IT practices with standards like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR. This approach lowers breach risks, reduces legal exposure, and ensures businesses can pass audits with confidence.
Cybersecurity Monitoring and Remediation
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, businesses rely on managed IT services to deliver real-time monitoring and rapid remediation. Providers continuously track networks for suspicious behavior, isolate compromised devices, block malicious IPs, and deploy patches before vulnerabilities are exploited. With the support of threat intelligence, automated response tools, and ongoing security assessments, they help organizations reduce breach risks, minimize downtime, and maintain compliance. This proactive protection strengthens overall resilience and ensures a more secure technology environment.
Data Protection and Recovery
Data loss or corruption can halt operations, and managed IT services reduce this risk through comprehensive data protection and recovery strategies. Providers encrypt sensitive information, schedule frequent backups to secure cloud or offsite locations, and perform recovery testing to verify systems can be restored quickly. They also define recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to set clear expectations for business continuity. These safeguards minimize downtime, ensure compliance with regulations, and keep organizations resilient during cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Through managed IT services, businesses gain the expertise needed to meet strict regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, PCI-DSS, and SOC 2. Providers configure systems for compliance, enforce security policies, maintain audit logs, and prepare documentation for inspections. They also perform risk assessments, monitor systems for policy violations, and update controls as standards evolve. In many cases, providers assist with staff training to improve awareness. This comprehensive approach reduces legal risk, improves audit success, and protects organizational reputation through accountable IT practices.
Co-Managed and Outsourced IT Models
Managed IT services can be delivered through co-managed or fully outsourced models, depending on a business’s needs. In a co-managed setup, providers work alongside internal IT teams to share responsibilities and fill skill gaps. Fully outsourced models, by contrast, transfer all IT operations to the provider for end-to-end coverage. Each approach offers different levels of control, scalability, and cost, giving organizations flexibility in how they structure IT management, which makes it important to understand the differences between managed IT services and co-managed IT services.
What is Co-Managed IT?
Co-managed IT is a hybrid service model where a managed service provider works alongside an internal IT team to share responsibilities. Providers often manage routine tasks such as system monitoring, patching, backups, or help desk support, while in-house staff focus on strategy, innovation, and high-priority projects. This model is especially useful for businesses with limited staff or expertise, as it provides access to specialized skills, extra coverage during peak demand, and scalable support. At the same time, companies retain control over core systems and decision-making.
Fully Outsourced Support Models
A fully outsourced IT model places all technology operations under the management of a service provider, giving businesses end-to-end coverage. In this setup, the provider assumes responsibility for infrastructure monitoring, cybersecurity, help desk support, backups, and even long-term IT planning. This model is particularly beneficial for small and mid-sized businesses without internal IT teams, as it delivers enterprise-level expertise at predictable costs. By relying on the provider’s resources, organizations gain scalability, 24/7 support, and reduced overhead while focusing entirely on core business goals.
Pros and Cons: Co-Managed vs Fully Outsourced
Both co-managed and fully outsourced IT models deliver significant advantages, but each comes with trade-offs that organizations need to weigh against their goals and internal capabilities.
| Model | Pros | Cons |
| Co-Managed IT | – Retains internal control – Adds flexibility – Fills skill gaps – Supports scalability | – Requires coordination between the internal IT team and the service provider – Risk of overlapping roles/costs |
| Fully Outsourced IT | – End-to-end coverage – Cost predictability – 24/7 support – Access to broad expertise | – Reduced direct control – Higher dependency on the provider – Potential vendor lock-in |
Future of Managed IT Services
The future of managed IT services lies in smarter, more secure, and more integrated solutions. MSPs are evolving from traditional support roles into strategic partners, using AI, automation, and unified platforms to deliver greater efficiency and resilience. As cyber threats intensify and business needs grow more complex, organizations will increasingly depend on providers that can anticipate issues, safeguard operations, and enable scalable growth.
AI-Driven Services and Automation
The next generation of managed services will be built on intelligence. Automation and AI are transforming MSP operations from reactive to proactive, with intelligent monitoring, self-healing systems, and predictive analytics reducing downtime and freeing IT teams for higher-value work.
By 2026, over 60% of infrastructure leaders are expected to adopt AI-ops tools to streamline service delivery. This shift positions MSPs as innovation partners, embedding intelligence into everyday IT functions. Businesses that embrace AI-driven services will not only cut costs but also gain the agility to scale and adapt faster than competitors.
Cyber Resilience and Security-First Architectures
Security is rapidly becoming the defining metric of MSP value. Cyber resilience is now central to managed IT services, with providers embedding security at every layer through automation, real-time threat intelligence, and zero-trust frameworks that minimize risk. The payoff is substantial: IBM reports organizations with fully automated security save an average of $1.76M per breach.
As attacks grow more sophisticated, businesses will increasingly rely on providers who prioritize resilience by design. The evolution ahead is clear. Security will shift from being a standalone function to the foundation of all managed service offerings.
Platform Consolidation and Predictive Insights
Complexity is driving a move toward unified, platform-based service models. The future MSP approach is focused on consolidating monitoring, security, collaboration, and analytics into integrated ecosystems that reduce vendor sprawl.
By 2027, IDC expects 75% of enterprises will demand these platform-based solutions for greater efficiency and ROI. With connected data streams, MSPs can forecast problems before they occur and continuously optimize IT performance. For businesses, selecting providers that deliver cohesive, predictive platforms will be essential for unlocking long-term value and scalability.
What to Look for in a Managed Service Provider (MSP)?
The most important qualities to look for in an MSP are certifications, responsiveness, and proven client satisfaction, as these directly reflect the provider’s ability to deliver secure, reliable, and cost-effective IT support. The right Managed Service Providers combine technical expertise with strong accountability and a track record of long-term partnerships.
Certifications and Proven Expertise
An MSP should hold recognized certifications such as Microsoft Gold or Solutions Partner, Cisco Premier/Gold, CompTIA Security Trustmark+, or ISO 27001 for information security. These credentials confirm the provider’s technical depth, compliance maturity, and ability to manage modern IT environments. Businesses should also ask about staff qualifications, such as Microsoft Certified Engineers or AWS Certified Solutions Architects, to ensure the provider’s team is skilled in the platforms they rely on.
Responsiveness and SLAs
A dependable MSP must provide service level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee specific metrics such as average response time (e.g., 15 minutes for critical tickets), escalation timelines, and minimum uptime (typically 99.9% or higher). Businesses should also confirm whether the provider offers 24/7 helpdesk support, remote monitoring, and on-site assistance for urgent issues. A well-structured SLA not only sets expectations but also holds the MSP accountable for performance.
Client Retention and Reviews
A quality MSP will demonstrate client retention rates above 90%, multi-year partnerships, and documented customer success stories. Prospective clients should look for third-party ratings (such as Gartner Peer Insights or Clutch reviews), detailed case studies, and reference clients in similar industries. These indicators provide confidence that the MSP consistently delivers value, adapts to evolving needs, and maintains strong, long-term relationships.
In conclusion, choosing the right MSP is key to ensuring reliable IT support and long-term success. By focusing on certifications, responsiveness, and proven client satisfaction, businesses can partner with trusted managed service providers to meet their unique needs and drive growth.